The college admissions process can be unfair due to different biases. While changes are being made, studies show that human biases, like favoritism for legacy students and wealthier families, still affect decisions.
- Legacy students are 7 times more likely to be admitted to top colleges like Harvard and make up nearly a third of the incoming class, with 70% being white. In 2023, 15.4% of Stanford’s incoming class benefited from legacy connections.
- A 2023 study found that children from the top 1% of families are twice as likely to attend Ivy League or top universities as those from middle-class families with similar test scores.
- A study from Indiana University found that SAT and GRE scores don’t predict success equally across all colleges. Race and gender can change how test scores predict GPA, leading to unfair differences in admissions.
These biases underscore the challenges in making the process fair, but AI has the potential to help reduce bias in college admissions and make decisions more equitable and accurate.
Understanding Forms of Bias in College Admissions
Human biases can impact the fairness and diversity of university admissions. These forms of bias in admissions, whether intentional or not, can lead to unfair advantages for some applicants while disadvantaging others.
Halo Effect
People often assume attractive individuals are smarter. Research from the University of St Andrews suggests admissions officers may favor good-looking applicants, even if others have similar qualifications.
Ingroup Bias
Some universities favor children of alumni over other equally qualified applicants. A survey found that 25% of admissions officers felt pressure to admit these students.
Stereotype Bias
Stereotypes about race or background can affect admissions decisions. A study found Asian American students were 28% less likely to be admitted than White students with the same qualifications.
Status Quo Bias
Wealthier students have better access to education and tutors, giving them an advantage in college admissions. Top universities like MIT, Georgetown, and Penn admit more wealthy students, making it harder for low-income students to compete.
Confirmation Bias
People look for information that supports what they already believe. In the University of California lawsuit, White and Asian students said they were treated unfairly compared to Black and Hispanic students. Such biases can lead to unfair decisions in the admissions process.
Groupthink (Bandwagon Effect)
Admission officers may follow others’ opinions instead of making independent decisions. If one reviewer praises an applicant, others might do the same without evaluation.
Recency Bias
Recent applications may get more attention than earlier ones. A strong applicant reviewed last might get more attention than an equally good one reviewed earlier.
While efforts to reduce bias in college admissions have been made, it’s difficult to remove them entirely. This is where AI can step in, providing a fairer and more consistent method of evaluating applications using objective data instead of personal opinions.
Role of AI in Admissions and Enrollment
AI in admissions is transforming how universities evaluate applicants, helping reduce bias in college admissions. Here’s how AI can improve the process:
Efficient Application Review
AI is transforming admissions by automating application screening. A survey found that 50% of admissions offices already use AI for this process. AI tools evaluate applications, assess academic records, and ensure unbiased evaluations. This reduces manual effort and speeds up decision-making. With EDMO’s Document Intelligence, universities can make admissions even more efficient by automating document processing, improving accuracy, and easily integrating with existing systems.
Source: Campus technology
Enhanced Communication with Applicants
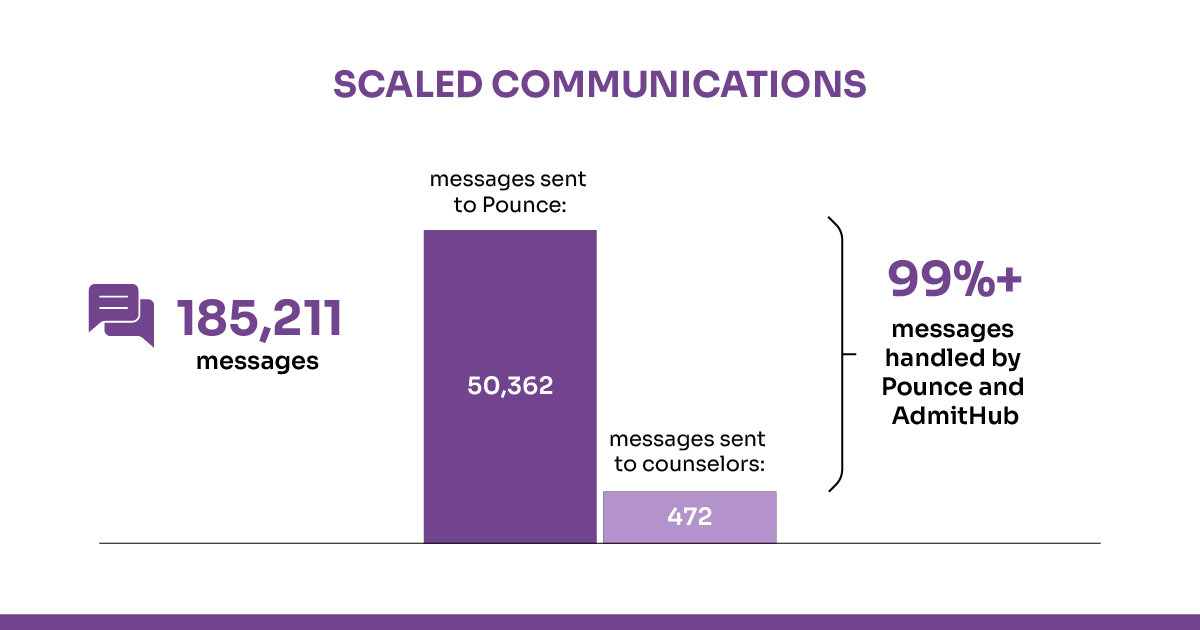
AI-powered chatbots are improving communication between universities and applicants. Georgia State University’s AI chatbot Pounce helped reduce summer melt by sending reminders and answering queries, resulting in a 3.3% increase in enrollment and a 21% decrease in summer melt. AI provides applicants with quick responses and guidance, improving engagement.
With EDMO’s Conversation Intelligence, universities can improve applicant communication, providing real-time support and ultimately increasing the application-to-enrollment rate by 5%.
Predictive Analytics for Student Success
AI-powered predictive analytics are helping colleges boost student success by identifying those at risk of dropping out. Georgia State University uses this system to monitor over 800 risk factors, leading to a 22% increase in graduation rates. By predicting academic challenges early, universities can provide support to improve student success and retention.
Better Decision Making
AI helps universities make better decisions by evaluating data from various sources like admissions, student performance, and engagement. For example, the University of Iowa used data analytics to improve its admissions strategy, leading to a 20% increase in out-of-state enrollments. This helps universities improve enrollment, allocate resources better, and improve programs.
Improved Student Retention
AI is helping universities improve student retention by identifying at-risk students early. For example, Nova Southeastern University in Florida used AI to detect students who might be at risk of dropping out. This proactive approach helped the university to provide early intervention through academic and support services, leading to a 17% reduction in student attrition. By addressing issues before they become serious, AI contributes to higher retention rates.
Source: Aible
Conclusion
Human biases have always been a problem in admissions, but AI can make it more fair and unbiased. By automating application reviews, bolstering communication, and using predictive analytics, AI ensures that decisions are based on facts rather than personal opinions. However, AI also has its challenges. If it learns from biased data, it could repeat unfair patterns, continuing bias in college admissions. Combining AI with human judgment is essential to keep the process fair and inclusive. EDMO’s AI solutions help universities make fair, data-driven decisions while ensuring transparency. Trusted by 200+ institutions, EDMO streamlines admissions and promotes inclusivity.
FAQs
Question 1: What is admission bias?
Answer: Admission bias occurs when certain applicants receive unfair advantages or disadvantages based on factors unrelated to their qualifications, such as race, gender, socioeconomic status, or personal connections.
Question 2: Can college admissions officers be biased?
Answer: Admissions officers are trained to be fair, but hidden biases can still affect their decisions without them realizing it.
Question 3. What is selection bias in education?
Answer: Selection bias in education occurs when certain students have a better chance of getting admitted due to factors like wealth, family connections, or race, making the process unfair.
Also Read:
EDMO inks partnership with Anunaad Public School to assist potential study abroad students
K-12 Guide | Empower your advisors with the Power of Technology
Fisher College collaborates with EDMO to boost their student engagement and admission strategy
EDMO Partners with Tinsukia Commerce College to Simplify Study Abroad Applications







