Table Of Contents
- 1Introduction
- 2What is AI and Why Does It Matter in Higher Education?
- 3Benefits of AI in Higher Education
- 4Challenges Facing AI Adoption in Higher Education
- 515 Ways AI Will Transform Higher Education
- 6Successful AI Examples in Higher Education That Can Inspire Our Future
- 7How to Implement AI in Higher Education
- 8Measuring the ROI of AI in Higher Education
- 9EDMO’s AI-Enhanced Solutions for Higher Education
- 10 Conversation Intelligence (CI): AI Engagement Layer for Students & Staff
- 11 System Intelligence – Connecting CRM, SIS, LMS into One Brain
- 12Summary
Introduction
AI in higher education is no longer a pilot experiment, it’s becoming the new operating system for universities. The global AI-in-education market is already valued at around $7 billion in 2025 and is projected to cross $100 billion by 2034, driven by demand for personalization and automation.
At the same time, over 80–85% of students worldwide report using AI tools regularly for their studies, from research to writing support. Faculty adoption is rising just as fast, with nearly 45% of higher-ed instructors now using AI in the classroom, up from about a quarter in 2023.
Real-world examples show what’s possible, Georgia State University’s “Pounce” chatbot cut summer melt from 19% to 9% by handling thousands of student queries automatically, while Arizona State University is rolling out campus-wide access to ChatGPT Edu to personalize learning and support at scale. Together, these trends are redefining how universities recruit, teach, support, and retain students.
What is AI and Why Does It Matter in Higher Education?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the ability of machines and software to perform tasks that usually require human intelligence, like understanding language, recognizing patterns, learning from data, and making decisions. Instead of following only fixed rules, AI systems improve over time as they process more information. This makes them powerful for handling complex, repetitive, or large-scale tasks that humans struggle to manage quickly or consistently.
Because Student Expectations Have Changed
Today’s learners expect instant responses, personalized guidance, and digital convenience. Traditional university systems simply can’t keep up with the volume or speed. AI fills this gap by matching student expectations in real time.
Because Higher Ed Is Overwhelmed With Data
Admissions, advising, enrollment, academic records, support tickets—universities generate millions of data points. Humans can’t process these at scale. AI makes sense of the chaos and converts raw data into actionable insights.
Because Staff Workloads Are at a Breaking Point
Admissions teams handle thousands of applications, repetitive questions, and manual tasks. AI takes over the high-volume, low-value work so staff can focus on decisions that genuinely require human judgment.
Because Student Fraud & Security Risks Are Rising
With a surge in online applications, identity fraud, document tampering, and ghost applicants, these threats are becoming real. AI-driven verification detects anomalies faster than any manual process.
Because Competition for Students Is Fierce
Institutions worldwide are fighting for the same shrinking pool of students. AI helps universities understand intent, predict enrollment, and offer personalized engagement—critical for staying competitive.
Benefits of AI in Higher Education
AI is quietly becoming the “second brain” of modern universities. It doesn’t replace people; it supercharges them. From attracting the right students to keeping them on track and reducing staff overload, AI helps institutions work smarter, respond faster, and deliver a more personalized, student-centric experience at scale.
Personalized Learning for Every Student
AI-powered platforms adapt content, difficulty, and pace based on each learner’s progress. Students get tailored recommendations for readings, videos, and practice questions, which boost engagement, confidence, and completion rates—especially in large classes where 1:1 attention is hard to come by.
24/7 Student Support and Guidance
AI chatbots and copilots answer FAQs, track application status, send reminders, and guide students through registration or financial aid—even at midnight before a deadline. This reduces students’ anxiety and drastically cuts support team ticket volumes.
Higher Retention and Reduced Dropouts
Predictive analytics identify at-risk students early by monitoring attendance, LMS activity, grades, and engagement. Advisors can then step in with timely outreach, tutoring, or wellness support—turning silent disengagement into a chance for retention.
Faster, Error-Reduced Administrative Work
AI automates repetitive tasks like document verification, GPA calculations, eligibility checks, and appointment scheduling. This shortens processing times from days or weeks to minutes, minimizes human error, and frees staff to focus on strategic, human-centred work.
Smarter Enrollment and Recruitment Decisions
By analyzing lead sources, behaviour, communication history, and demographics, AI highlights high-intent prospects and predicts which students are most likely to enroll. Admissions and marketing teams can then prioritize follow-ups and campaigns with the highest ROI.
Data-Driven Strategic Planning
AI tools help leaders forecast enrollment, optimize course offerings, and allocate faculty, classrooms, and budgets more effectively. Instead of relying on gut feeling or outdated reports, decision-makers get real-time, actionable insights across the student lifecycle.
Challenges Facing AI Adoption in Higher Education
AI sounds exciting, but implementing it on campus is rarely straightforward. Universities must balance innovation with ethics, data protection, academic integrity, and staff readiness, all while working within tight budgets and legacy systems. These challenges don’t make AI impossible; they just mean institutions need a thoughtful, strategic approach rather than quick, isolated pilots.
Data Privacy and Security
AI thrives on data, and universities have gold mines of sensitive information: demographics, grades, financial aid, health details, and even behavioural data from LMS and CRMs.
Why it’s a problem:
- Every new AI tool is another system that touches student data, increasing the risk of breaches, leaks, or misuse.
- Regulations such as FERPA, GDPR, and local data laws require strict controls on where data is stored, how it’s processed, and who can access it.
- Many AI vendors use cloud infrastructure and may store data in other countries, which can trigger legal and compliance headaches.
What it means in practice:
IT, legal, and leadership need to vet vendors, set strict data-sharing contracts, anonymize data wherever possible, and continuously monitor for security threats. Without this, even a helpful AI chatbot can become a liability.
Academic Integrity and Misuse
Generative AI tools (ChatGPT-style) make it easy for students to get instant essays, code, and homework answers.
Why it’s a problem:
- Traditional assignments (essays, take-home exams, basic coding tasks) are suddenly much easier to outsource to AI.
- Faculty fear that grades may no longer reflect genuine learning or effort.
- Detection tools are imperfect, can give false positives, and can’t keep up with rapidly evolving models.
What it means in practice:
Universities must rethink assessment design (more oral exams, in-class work, projects, drafts), set clear AI-use policies (what’s allowed vs. not), and educate students on ethical use. Otherwise, AI feels like a threat rather than a learning aid.
Bias and Fairness in Algorithms
AI systems learn from historical data, and history isn’t always fair.
Why it’s a problem:
- If models are trained on biased data (e.g., past admissions or grading patterns), they can reinforce those inequities.
- Predictive systems that flag “at-risk” students may penalize certain groups more often, just because they fit patterns from historical data.
- Black-box algorithms make it hard to explain why a student was classified a certain way.
What it means in practice:
Institutions need processes to audit AI models regularly, demand transparency from vendors, test outcomes across different demographic groups, and include ethicists and diverse stakeholders in designing and approving AI use cases.
Change Management and Faculty Resistance
Even the best AI tool fails if people don’t use it.
Why it’s a problem:
- Faculty worry AI will replace teaching, reduce academic rigour, or add extra administrative work.
- Many staff feel overwhelmed by the constant stream of “new tools” when they’re already stretched thin.
- Training and support are often an afterthought—tools are rolled out with a webinar and an email, then left to fend for themselves.
What it means in practice:
Successful AI projects treat faculty and staff as partners, not obstacles, by offering hands-on training, demonstrating time savings, addressing concerns openly, and involving them early in tool selection and pilot design. Without buy-in, adoption stays shallow and scattered.
Legacy Systems and Integration Issues
AI works best when it can “see” data across CRM, SIS, LMS, email, advising tools, and more, but most universities live in tech silos.
Why it’s a problem:
- Old systems don’t always have clean APIs or standardized data structures.
- Integrations can take months, require custom development, and cost more than the AI license itself.
- If systems don’t sync properly, AI tools get incomplete or outdated data, leading to wrong insights or broken automations.
What it means in practice:
IT teams need time, budget, and a clear integration strategy. Sometimes the real project isn’t “AI deployment”—it’s cleaning data, standardizing fields, and modernizing infrastructure so AI can actually work as promised.
Cost, Budget Constraints, and ROI Pressure
AI is sold as “cost-saving,” but there’s a bill before the savings show up.
Why it’s a problem:
- Costs include licenses, implementation, integrations, training, governance, and ongoing support.
- Funding cycles in higher ed are slow, and many budgets are already stretched.
- Leadership wants a clear ROI: more enrollments, better retention, or measurable efficiency gains—not just “innovation.”
What it means in practice:
Universities must pick focused use cases (e.g., reducing application processing time, boosting lead conversion) and track metrics from day one. Without quantifiable outcomes, AI pilots risk being seen as expensive experiments that get cut in the following budget review.
Ethical, Policy, and Governance Gaps
AI is moving faster than university policy committees.
Why it’s a problem:
- Many institutions lack a unified AI policy covering teaching, research, student use, and administrative use.
- Departments often experiment independently with different tools, creating a patchwork of practices and risks.
- There are open questions around transparency (Do we tell students when AI is used?), consent, and accountability (Who’s responsible if AI makes a harmful recommendation?).
What it means in practice:
Universities need formal AI governance frameworks—with cross-functional committees (IT, academic leadership, legal, student reps), clear guidelines for procurement and use, and regular reviews. This turns AI from “random experiments” into a managed, strategic capability.
15 Ways AI Will Transform Higher Education

AI is set to move universities from slow, manual processes to innovative, data-driven ecosystems. As AI-in-education investment surges globally and tools like chatbots, predictive analytics, and AI copilots go mainstream, institutions will be able to personalize learning, automate admissions, and support students 24/7, without proportionally increasing staff. Below are 15 concrete ways AI will reshape higher education across teaching, student success, and operations.
Hyper-Personalized Learning Paths
AI systems continuously analyse a student’s quiz results, time-on-task, clicks, and past performance to understand where they struggle or excel. Based on this, the system can reorder modules, suggest remedial content, or even adjust the pace. Instead of one syllabus for everyone, each student gets a dynamic path tailored to their needs.
Intelligent Tutoring and Study Support
AI tutors act like 24/7 teaching assistants. Students can ask questions in natural language (“I don’t get this step in the proof”) and receive explanations, examples, or step-by-step breakdowns. Over time, the AI can adjust its explanations based on how the student responded previously, making support more adaptive than static FAQs or PDFs.
Smarter, Data-Driven Admissions
AI can scan thousands of applications, documents, and interaction histories to prioritize which applicants need review first or are most likely to enroll. It doesn’t make the final decision, but it surfaces patterns, such as strong academic fit, high engagement, or scholarship sensitivity so that admissions teams can spend their time on nuanced judgment calls rather than basic triage.
Always-On Student Support (Chatbots & Copilots)
Instead of waiting for office hours, students can ask chatbots about deadlines, course registration, housing, fees, or campus services at any time. These AI agents can pull answers from institutional policies, websites, and SIS/CRM data. For complex cases, they route students to the right office, reducing frustration and freeing staff from repetitive “where do I find…” questions.
Early-Warning Systems for At-Risk Students
Predictive models can combine attendance, LMS logins, assignment submissions, grades, and even engagement in discussion boards to detect patterns that often precede failure or withdrawal. When risk scores rise, advisors receive alerts and can intervene proactively via email, phone, or in-person meetings. This turns student success from reactive “post-failure” support into prevention.
Automated Grading and Feedback
AI can auto-grade objective questions (MCQs, matching, coding output) and provide formative feedback on writing, structure, and grammar. Faculty still control the final grade, but AI speeds up the initial pass and provides students with quicker feedback loops. In large classes, this means students don’t wait weeks to find out where they went wrong.
AI-Enhanced Course Design
By analysing which questions students commonly miss, where they drop off in videos, and which activities correlate with success, AI provides instructors deep insight into course effectiveness. Generative tools can help them create new quiz questions, alternative explanations, or differentiated assignments. Over time, courses evolve based on real student behaviour rather than guesswork.
Accessible and Inclusive Learning Experiences
AI can auto-generate captions, transcripts, translations, and audio versions of content, making it easier for students with hearing, visual, language, or learning differences to participate fully. It can also simplify complex texts or provide visual summaries for students who benefit from different formats. This lowers barriers without requiring instructors to manually create every adaptation.
Streamlined Administrative Workflows
Tasks such as verifying identity, checking document completeness, converting international grades to local scales, or calculating GPAs are rule-based and repetitive, making them ideal for AI. Instead of staff manually entering data and cross-checking it, AI can process documents in bulk, flag exceptions, and push clean data into SIS/CRM systems. This shrinks turnaround times and reduces fatigue errors.
Intelligent Enrollment and Yield Management
AI can model the whole recruitment funnel: which channels bring serious applicants, where prospects drop off, and which communication nudges increase conversions. It helps teams decide where to focus budget (events, email, digital ads) and which students to call or text personally. The result is higher enrollment with more efficient use of limited recruitment resources.
Personalized Career and Pathway Guidance
Instead of generic advice like “consider business or engineering,” AI can analyse a student’s interests, coursework, grades, and even co-curricular activities to suggest majors, minors, micro-credentials, and career tracks. It can also show labour-market demand and salary ranges, helping students make more informed choices and reducing last-minute central switching that delays graduation.
AI-Powered Research Support
Researchers can use AI to rapidly summarise literature, extract key findings, generate hypotheses, and even assist with code or data cleaning. While humans still design the study and interpret the results, AI reduces the time spent on tedious tasks such as reference formatting, initial data exploration, and drafting boilerplate sections.
Smarter Campus Operations and Resource Planning
AI can analyse historical data on enrollments, room usage, course fill rates, and exam schedules to recommend optimal timetables and resource allocation. It can help avoid over-filled sections, under-used rooms, or last-minute schedule chaos. Facilities, IT, and academic planning teams benefit from more accurate forecasts instead of relying on static spreadsheets.
New Models of Teaching and Assessment
Because AI can handle content delivery, feedback, and some grading, faculty can redesign courses around projects, discussions, simulations, and real-world problems. Assessment can focus more on critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration, while AI supports the routine checks. Teachers shift from “lecturers” to “learning designers and mentors.”
Stronger Student Experience and Well-Being
When academic, engagement, and support data are connected (ethically and with consent), AI can identify students who show signs of educational or social withdrawal. It can nudge them toward tutoring, counselling, or peer support before issues escalate. This creates a campus environment that feels more responsive and caring, even at large institutions.
Successful AI Examples in Higher Education That Can Inspire Our Future
AI in higher education isn’t just theory anymore, universities across the world are already using it to cut melt, boost support, and scale personalization. From chatbots that send 185,000 messages over one summer to campus-wide AI copilots, these real deployments show what “AI done right” can look like and give a roadmap for institutions planning their own transformation.
Georgia State University – Pounce Chatbot and Summer Melt
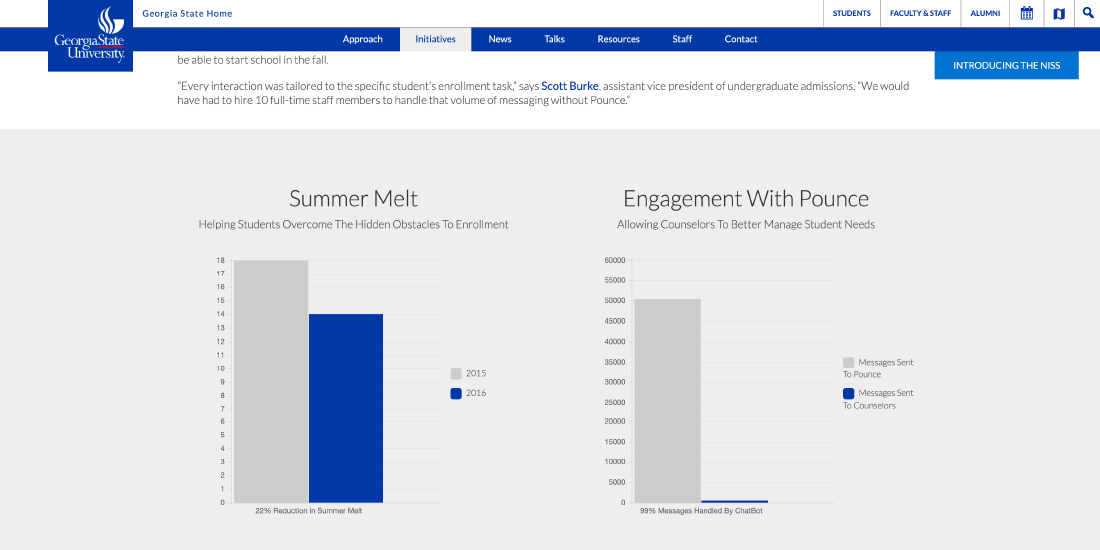
Georgia State worked with an AI texting chatbot called Pounce to support incoming first-year students over the summer. The bot sends reminders about forms, financial aid, immunization, housing, and deadlines, and answers questions 24/7 via SMS.
- In its first summer, Pounce exchanged around 185,000 messages with students—far beyond what any human team could handle.
- This outreach helped reduce summer melt from about 19% to 9%, meaning more admitted students actually enrolled.
AI chatbots can protect enrollment revenue by catching “I got stuck on a form” issues before students quietly disappear.
Arizona State University – Campus-Wide ChatGPT Edu
Arizona State University (ASU), one of the largest public universities in the U.S., has partnered with OpenAI to deploy ChatGPT Edu across teaching, research, and operations.
- The tool is available to students, faculty, researchers, and staff and is embedded in their “Digital Backpack” ecosystem.
- Use cases include personalized tutoring, drafting and summarising content, research support (e.g., grant-writing help), and admin automation under an enterprise agreement that doesn’t use ASU data to train public models.
ASU shows how AI can be rolled out as institutional infrastructure, not just a side tool students use on their own.
California State University System – AI Tutoring at Massive Scale
OpenAI is rolling out ChatGPT Edu to the California State University (CSU) system, covering about 500,000 students and faculty across 23 campuses.
- Students can use AI for personalized tutoring and study guides, while faculty can use it to support administrative tasks, such as drafting materials or organizing course resources.
- The move builds on earlier success of ChatGPT Enterprise in other universities, motivating a dedicated education-focused version (ChatGPT Edu).
CSU illustrates how AI can support huge public systems where scaling human support alone would be financially impossible.
Staffordshire University (UK) – Beacon Digital Coach
Staffordshire University launched Beacon, a smartphone-based digital assistant hosted on Microsoft Azure.
- Beacon acts as an “intelligent digital guide” to student life: it shows timetables, answers more than 400 FAQs on services and facilities, and connects students to their personal tutors.
- It can even check in on student mood and alert staff if a student might need support, helping the university spot wellbeing risks earlier.
Beacon is a strong example of AI being used not only for admin questions but also for wellbeing, belonging, and day-to-day campus navigation.
Deakin University (Australia) – Genie Virtual Assistant
Deakin University built Genie, a digital personal assistant powered partly by IBM Watson, voice recognition, and predictive analytics.
- Genie lives in a mobile app and helps students manage schedules, assignments, deadlines, and general university life—a kind of “Siri for Deakin.”
- Students ask Genie around 1,600 questions a week, getting 24/7 answers about studying on campus or in the cloud.
- The project has won global recognition, including a Digital Edge 50 award for digital innovation.
Genie shows how AI can sit at the centre of a mobile-first, student-centric experience, blending academic, admin, and lifestyle support.
How to Implement AI in Higher Education
AI implementation isn’t about “adding a chatbot,” it’s about solving real institutional problems with smarter, data-driven workflows. Successful universities start with clear goals, build the right team and guardrails, run focused pilots, and then scale what works across the campus.
Define Clear Goals and Priority Use Cases
Start by naming exactly what you want AI to fix. For example: “reduce application processing time by 50%,” “cut summer melt by 5 points,” or “halve response time for student queries.” Then pick 2–3 use cases that directly support those goals (example, an admissions chatbot, an early-alert system, or document automation). This keeps you away from vague “AI innovation” and anchors every decision to measurable impact.
Create a Cross-Functional AI Team and Governance
AI touches IT, academics, legal, and student experience, so you need a shared steering group. Include IT/data leaders, faculty, enrollment or student services, legal/compliance, and at least one student voice. This team defines AI principles (privacy, fairness, transparency), approves pilots, and sets ground rules for tools and vendors. Good governance prevents random, risky experiments and builds trust across campus.
Get Data and Systems Ready for AI
Even the best AI fails on messy, siloed data. Map where key information lives CRM, SIS, LMS, finance, spreadsheets and check how well these systems talk to each other. Prioritize integrations and data cleaning for the use cases you chose: for example, connecting your chatbot to CRM for status updates, or your early-alert model to LMS and SIS. The rule is to start with “enough” data quality and connectivity to deliver reliable results, then improve as you go.
Run Small, Measurable Pilots (Not Campus-Wide Experiments)
Pick 1–2 pilots where risk is low, and outcomes are easy to measure like automating FAQs, triaging support tickets, or processing transcripts. Define owner, timeline, and success metrics before launch (e.g., staff hours saved, response-time reduction, melt/retention impact, satisfaction scores). Involve frontline users in testing and iterate quickly on prompts, workflows, and UI. The goal is to prove value in months, not years, and use real data to convince skeptics.
Train People, Communicate Clearly, and Scale What Works
AI adoption lives or dies on people, not models. Offer hands-on training showing concrete time-savers (“here’s how to draft emails,” “here’s how to see at-risk students”). Explain where AI is used, what data it sees, and how humans still oversee decisions. Once a pilot consistently hits its targets, formalize it, integrate it into core systems, document processes, expand to more departments, and update policies. Equally important, retire tools that don’t deliver. Scale the winners, sunset the rest.
Measuring the ROI of AI in Higher Education
For universities, AI can’t just be a shiny experiment—it has to pay off. Measuring ROI means proving that AI improves student success, reduces operational costs, and optimises resource use. With the right metrics and case-based evidence, institutions can demonstrate that AI is not just innovative but also financially and strategically essential.
Track Core Outcome Metrics
Start with the big three: student success, operational efficiency, and resource optimization. Measure changes in retention and graduation rates, processing times for administrative tasks, and utilization of classrooms, staff, and energy before vs after AI deployment. AI used in adaptive learning, predictive analytics, and campus management should show concrete gains in these metrics.
Quantify Financial Impact
Convert improvements into money. Reduced manual workloads → fewer overtime hours or avoided hires; better retention → more tuition preserved; optimized facilities and energy usage → lower operating costs. SmartDev notes that AI-driven campus and process optimisation can directly reduce operational expenses and strengthen institutional financial health when systematically tracked.
Use Real Case Studies as Benchmarks
Compare your results with proven examples: Georgia State used AI analytics to identify at-risk students, resulting in higher graduation rates and reduced attrition; Arizona State applied AI to campus management and energy, reporting millions in savings; Southern New Hampshire University leveraged adaptive learning to boost engagement and performance. These cases provide realistic targets for your own ROI expectations.
Build a Simple ROI Framework and Dashboard
For each AI project, define:
- Inputs: licenses, implementation, training, data work
- Outputs: hours saved, errors reduced, retention/enrollment changes, cost reductions
Then summarise in clear indicators: payback period, annual net benefit, and 3–5 key metrics visualised on a dashboard. This makes ROI visible and understandable for leadership, not just buried in reports.
Watch for Common ROI Pitfalls
SmartDev highlights two big blockers: poor data quality and weak stakeholder alignment. Incomplete or messy data produces unreliable AI predictions and undermines impact; rolling out tools without faculty and staff buy-in leads to low usage. To protect ROI, invest in data governance, involve end-users early, and treat training and change management as part of the AI budget, not an optional extra.
EDMO’s AI-Enhanced Solutions for Higher Education
EDMO turns your existing stack (Salesforce, Slate, SIS, LMS, portals) into an AI-powered admissions operating system. Its three pillars Document Intelligence , Conversation Intelligence), and System Intelligence work together to automate document review, personalize engagement, and keep data in sync across systems. Institutions using EDMO have processed 3M+ student documents, saved 7M+ manual hours, handled 20M+ conversations, and reduced costs by millions of dollars.
Document Intelligence (DI): Automating Application Evidence
Document Intelligence is EDMO’s suite of AI tools that reads, evaluates, and structures application materials, from transcripts and essays to ID documents, cutting evaluation time from weeks to hours while improving consistency and fairness.
Transfer Credit Evaluation
Processes complex transfer transcripts in minutes, maps previous coursework to your catalog, and clears backlogs quickly. It has already processed 210K+ transcripts and 1.6M+ credits, saving staff millions of hours and giving applicants faster, clearer credit decisions.
GPA Calculator
Converts international and domestic grades into a standardized GPA using global grading scales. This allows fair comparison across systems, reduces manual spreadsheet work, and speeds up admission decisions.
ID Verification
Automates ID checks by sending verification emails, collecting documents, and validating photo IDs with AI. Institutions can track status, flag mismatches, and detect fraud in minutes instead of days, without pulling staff off other tasks.
Email Doc Extractor
Scans admissions inboxes, pulls out attached documents, classifies them, and syncs key data into the CRM. The tool has processed 1.5M+ emails, synced 95K+ documents, and saved 150K+ staff hours and over $1M in costs.
Application Evaluator
Uses LLMs to analyze essays, SOPs, LORs, resumes, and transcripts, surfacing key strengths, risks, and fit signals for the admissions team. This makes holistic review more consistent and data-backed, while still leaving the final judgment to humans.
Interview Analyzer
Evaluates recorded or live interviews, extracts skills and sentiment, and produces structured insights. It helps committees compare candidates more objectively and focus their discussion on meaningful differences rather than note-taking.
Conversation Intelligence (CI): AI Engagement Layer for Students & Staff
Conversation Intelligence is EDMO’s AI communications layer that automates and personalizes outreach across email, SMS, and other channels so students get instant, relevant guidance while staff focus on high-value conversations. Institutions using CI report 20M+ conversations, 3M+ hours saved, $4M+ cost savings, and inquiry response times under 10 minutes.
Admissions Copilot
An AI-powered copilot/chatbot that handles 24/7 student support, answers FAQs, guides applicants through forms, and sends personalized nudges. It scores and prioritizes high-intent leads, so staff know who to call first, and integrates directly with Salesforce/Slate to keep records in sync.
Knowledge Source
Analyzes URLs, websites, policy pages, and long PDFs to give staff precise, instant answers inside tools like Slate. Instead of hunting through manuals or websites, advisors query Knowledge Source and get summarized insights they can use in calls, emails, or chats.
Admissions Agent
Sits at the intersection of CI and workflow automation. Admissions Agent turns outreach and follow-up logic into automated workflows, assigning tasks, sending reminders, and moving records through stages in manual, semi-autonomous, or fully autonomous modes. It reduces repetitive admin work and ensures no lead or task falls through the cracks.
System Intelligence – Connecting CRM, SIS, LMS into One Brain
System Intelligence is EDMO’s integration layer, the “wiring” that connects CRM, SIS, LMS, portals, and EDMO apps so AI always acts on complete, current data. With 18+ years of integration experience, 150K+ records synced, 1M+ automations triggered, and over $27M in efficiency and ops savings, it normalizes data into a unified student profile and orchestrates cross-system workflows and triggers. That means no more duplicate records, stale statuses, or “lost in the stack” students.
Summary
AI in higher education isn’t about replacing people with machines, it’s about giving students and staff the support they’ve always needed but never had the time or resources for. When done well, AI quietly takes over the repetitive, frustrating work so advisors can listen more, faculty can teach more, and students can get help the moment they need it not days later. Yes, there are real questions around ethics, privacy, and fairness, and they deserve serious attention. But with intentional design and responsible governance, AI can help universities feel more responsive, more personal, and ultimately more human.









No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
Leave a Comment