Discover how the higher education crisis in enrollment, fueled by rising costs and shifting perceptions, reshapes institutions. Learn actionable strategies to attract students, improve accessibility, and adapt to the evolving needs of today’s educational landscape.
Table Of Contents
The State of Education + Enrollment
An abject crisis in college enrollment in the United States, with sharp drops in several demographic groups, is a disconcerting picture. Between 2010 and 2021, undergraduate enrollment at degree-granting postsecondary institutions fell from 18.1 million to 15.4 million students, a 15% decline. Male students experienced a 17% drop in enrollment during this time, making the fall more noticeable.
In the fall of 2024, freshmen enrollment at U.S. institutions declined significantly. Freshmen enrollment at private nonprofit four-year colleges fell 6.5% from the previous year, while public four-year institutions lost 8.5%.
Declining birth rates, rising tuition prices, and changing views on the proverbial worth of a college degree are some of the causes influencing these changes. According to the National Center for Education Statistics, enrollment is expected to surge by 9% for both males and females between 2021 and 2031, which could reverse the trend.
Fig 1: Actual & projected undergraduate enrollment in degree-granting postsecondary institutions, by sex: Fall 2010 through Fall 2031
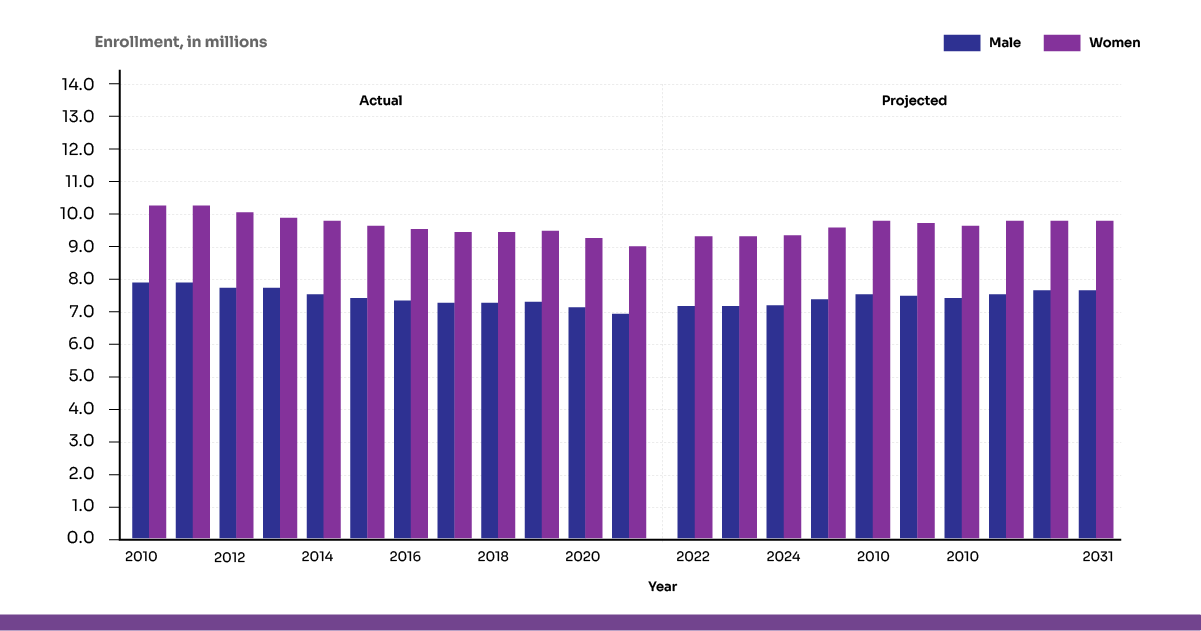
Addressing this crisis in enrollment is crucial for the sustainability of higher education institutions and the broader economy.
One Affects Institutions, the Other Affects Programs—Know the Difference
The term “crisis in enrollment” portrays a perennial issue with how students are enrolled in educational institutions that impact specific programs, populations, or institutions. A crisis in enrollment focuses on regional problems such as decreased enrollment in particular majors, underrepresentation of specific student groups, or administrative difficulties in admissions, as opposed to an enrollment crisis, which implies a global and systemic decline in student numbers.
Parameters | Enrollment Crisis | Crisis in Enrollment |
Definition | A significant and pervasive drop in student enrollment impacts universities’ operational and financial stability.
Example: The university is experiencing financial challenges due to a significant drop in student enrollment. Enrollment fell by almost 11% over nine years, which adds to the estimated $18 million shortfall in 2023. Since enrollment at the two-year branch college in Menasha has been drastically dropping, this financial burden has led to staff layoffs and plans to close the campus by spring 2025. | A particular enrollment problem, like a drop in a specific program, changes in the population, or administrative difficulties.
Example: The oldest historically Black university in Georgia, Savannah State, has struggled with financing and enrollment declines. As a result of these problems, the Board of Regents named Jermaine Whirl, president in 2024, decided to restore the university’s enrollment and financial situation. |
How AI is Addressing Higher Education’s Greatest Challenge: The Future of Enrollment
AI is transforming higher education by addressing one of its significant challenges: enrollment. As institutions grapple with declining student numbers, shifting demographics, and increasing competition, AI-driven solutions are assisting universities in attracting, engaging, and retaining students more effectively.
Predictive Analytics:
AI models examine past admissions data to uncover patterns and forecast future enrollment trends, allowing institutions to develop focused recruitment strategies. A large urban research university study utilized machine learning to predict admissions decisions, enhancing the understanding of factors influencing enrollment.
Marketing & Outreach:
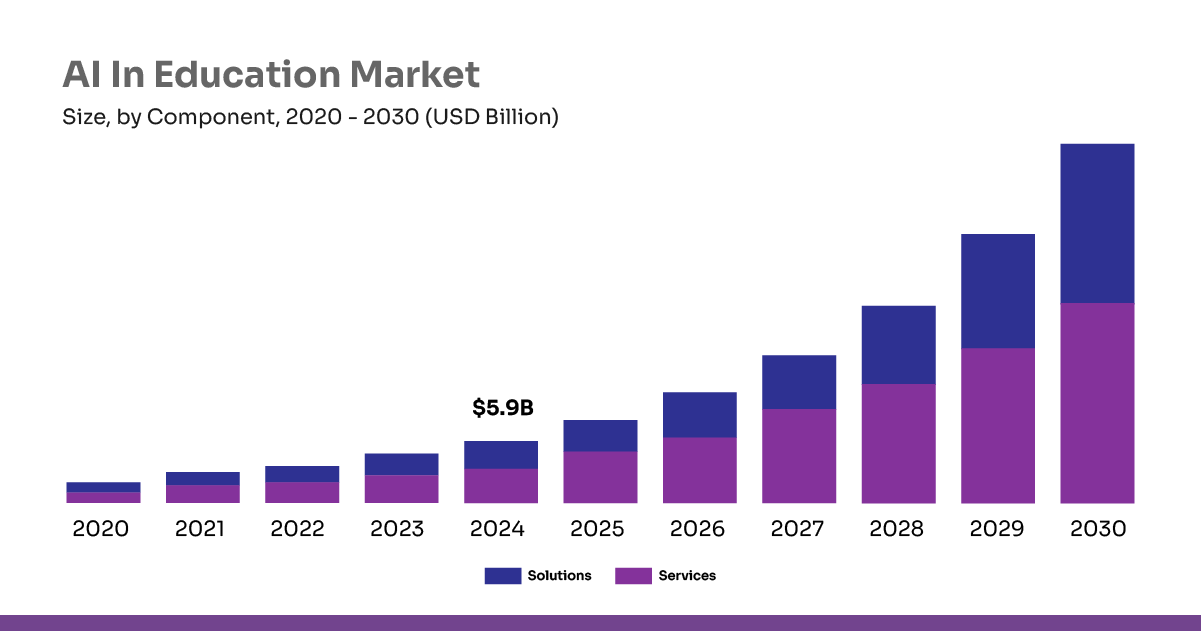
Customized marketing campaigns driven by AI aim to reach potential students more efficiently, enhancing engagement and application numbers. The global AI in education market was valued at $2.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $6 billion by 2025, indicating significant investment in AI-driven educational tools, including marketing applications.
Chatbots & Virtual Assistants:
Chatbots powered by AI offer immediate answers to questions from potential students, assisting them with the application process and enhancing their overall experience. Similarly, EDMO’s Conversation Intelligence transforms student interactions with AI-powered chatbots and voice assistants. These tools provide real-time, personalized support across various channels, managing everything from admissions inquiries to financial aid guidance. This automation guarantees that students receive accurate information instantly, enhancing their overall experience and boosting institutional efficiency. American higher-ed institutions are creating homegrown AI-powered chatbots for refined student engagement, administrative support, and document review. OpenAI’s deployment of ChatGPT across California State University’s 23 campuses aims to offer personalized tutoring and administrative assistance to 500,000 students and faculty, showcasing the scalability of AI solutions in education.
Retention & Student Support:
AI systems track student performance to detect individuals at risk of leaving school, enabling prompt actions to enhance retention rates. AI systems monitor student performance to identify those at risk of dropping out, allowing timely interventions to improve retention rates. For instance, AI predictive analytics have helped institutions reduce dropout rates by 20% in 2022.
Course & Program Innovation:
AI assesses employment market trends to suggest new courses and programs that align with current needs, drawing in more students. The AI in education market, valued at $5.88 billion in 2024, is projected to grow at a 31.2% CAGR (2025–2030) due to rising demand for personalized learning.
AI aligns courses with industry needs, enhancing coding, data analysis, and machine learning skills through adaptive, hands-on training programs.
Operational Efficiency:
Artificial intelligence simplifies administrative tasks like managing applications and scheduling classes, enabling staff to concentrate on strategic efforts to increase enrollment. The anticipated growth of AI in the education market to $6 billion by 2025 underscores the increasing adoption of AI tools to enhance operational efficiency in educational institutions.
Crisis Response Speed:
AI allows organizations to swiftly put strategies into place to tackle unexpected declines in enrollment, offering analytical insights for prompt intervention. For example, between 2016 and 2021, 61 colleges and universities closed or merged due to enrollment declines. To combat this trend, institutions are increasingly adopting AI tools to enhance recruitment and retention efforts. A survey revealed that 84% of higher education professionals reported using AI in their professional or personal lives.
Summary
With undergraduate enrollment falling 15% between 2010 and 2021 due to falling birth rates, growing costs, and shifting views on the value of higher education, the United States is experiencing a crisis concerning college enrollment. While enrollment crises affect specific programs or demographics, enrollment crises affect institutions as a whole. AI is becoming a significant answer, utilizing chatbots, retention tracking, tailored marketing, predictive analytics, and innovative programs to lock down enrollments and retain students. Institutions can adjust thanks to AI-driven administrative and crisis response efficiencies. Just like EDMO’s Document Intelligence and Conversation Intelligence, both play a crucial role in this transformation. Document Intelligence enhances student engagement and accelerates the enrollment process by providing advanced data analysis and insights. Meanwhile, Conversation Intelligence revolutionizes student interactions through AI-powered chatbots and voice assistants. Leveraging technology is essential for reversing declining enrollment and guaranteeing institutional sustainability, as AI in education is expected to develop dramatically.
Also Read: How the Trump Administration’s H1B Policy is Shaping Up – and What it Means for Your University
EDMO’s Conversational Intelligence Overhauls Info Gathering for US Knowledge-Sharing Platform
Demystifying SOP and Essay Analysis with AI Solutions
AI-Driven Career Pathways: Transforming Career Services for Graduates










No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
Leave a Comment