Student success is more than just grades—it encompasses academic performance, personal development, social engagement, and career readiness. By adopting evidence-based strategies, such as early engagement, personalized support, and holistic development programs, colleges and universities can help students thrive and achieve their full potential.
Table Of Contents
- 1Introduction
- 2What is Student Success in Higher Education
- 3Key Factors That Influence Student Success and Persistence
- 4How to Measure Student Success
- 5Measuring Student Success in Today’s World
- 6Tips to Improve Student Success in Higher Education
- 7Why Are Success Strategies Important for Students?
- 8Conclusion
Introduction
Student success has become a central focus for higher education institutions worldwide, but translating this priority into measurable outcomes remains a challenge. A recent survey found that while 59% of education leaders believe their institutions are highly effective in prioritizing student outcomes, only 44% feel confident in their ability to collect and analyze related data. This gap highlights the pressing need for more data-driven approaches and well-defined strategies to support students holistically.
What is Student Success in Higher Education
Student success in higher education refers to the continuous measurement and support of students’ academic performance and overall growth during their postsecondary journey. It is not limited to grades or graduation rates but also encompasses how students engage with peers, adapt to campus life, and utilize available resources to reach their full potential.
For institutions, defining success requires a clear understanding of:
- Who their students are on a personal and academic level
- What expectations they hold for their college experience
- Where they seek support and resources throughout their journey
While each generation of students has different needs and expectations, true success is measured by how well students grow in all areas of life—not just academics. In today’s world, student success is a combination of academic progress, personal growth, involvement in the community, and the ability to keep moving forward despite challenges.
Key Factors That Influence Student Success and Persistence
Student success, persistence, and retention don’t happen automatically. Every student has the potential to complete their degree, but their chances of success depend on several important factors. These include the quality of education, mental well-being, and access to support systems.
Quality of Academic Content and Teaching
For most students, the primary reason for attending college is to get a good education. While campus activities and living arrangements matter, classroom learning has the biggest impact.
The quality of education depends on:
- The textbooks and learning materials used
- The knowledge and expertise of instructors
- The teaching and evaluation methods applied
Research in the International Journal of Higher Education shows that effective teaching encourages curiosity, critical thinking, and helps students take ownership of their learning.
Mental Well-being and Relationships
A student’s mental and emotional health strongly affects their performance in college. Building healthy relationships, engaging in campus life, and having access to mental health services are essential for well-being.
A study by Ya-Hsin Hsiao (Western Kentucky University) found that psychological well-being is closely linked to GPA, especially for first-generation students. According to a U.S. News survey, about 70% of college students have struggled with mental health since starting their studies, highlighting the need for stronger support.

Support Networks and Resources
Students are more likely to succeed when they feel supported. Without guidance, they may struggle or even drop out when challenges arise.
That’s why universities provide resources such as:
- Academic advisors
- Peer mentors and faculty support
- Residence hall and campus life staff
- Counseling and mental health services
- Student clubs, organizations, and sports teams
- On-campus emergency support
For example, at the University of the Incarnate Word, students enrolled in the TRIO Student Support Services program achieved a 96% retention rate and were 15% more likely to graduate on time.
How to Measure Student Success
Measuring student success is vital for both students and institutions. For students, it ensures they receive the support needed to reach their goals. For institutions, it highlights strengths, identifies gaps, and drives improvements. By tracking outcomes year after year, colleges and universities can:
- Support at-risk and marginalized students
- Provide better training and tools for faculty
- Enhance the overall student experience
Accurate data also allows for personalized support, closing achievement gaps, and creating programs that meet evolving student needs. Below are some key ways to measure success:
Retention Rates
Retention rate tracks how many students return to the same institution the following year. It is one of the most common indicators of persistence and success.
Formula:
Retention Rate (%) = (Number of returning students ÷ Total number of students in a cohort) × 100
This data helps institutions adjust programs, allocate resources, and strengthen student engagement. By using predictive analytics, colleges can identify students who may be at risk of dropping out and intervene early with personalized support. Tools like Edmo Conversation Intelligence enhance this process by analyzing student interactions and engagement patterns to predict retention risks more accurately. For example, the State Technical College of Missouri reports a 90% retention rate, one of the highest in the U.S.
Graduation Rates
Graduation rate measures how many students complete their program within a specific timeframe (four to five years for undergraduates, shorter for postgraduates).
Formula:
Graduation Rate (%) = (Number of graduates ÷ Total number of students in a cohort) × 100
This metric reflects long-term outcomes and program effectiveness. On average, private nonprofit four-year colleges have a 76% graduation rate, public colleges 71%, while for-profit institutions lag at 36%.
Post-Graduation Employment
This measures how well students transition into the workforce. It includes data on:
- Percentage of graduates employed full-time in their field
- Average starting salary
- Time taken to secure employment
Employment outcomes show how effectively academic programs prepare students for real-world careers and help institutions align coursework with industry needs.
Student Support Services Usage
Support services such as tutoring, counseling, career guidance, and mentoring play a key role in success. Tracking usage helps identify which students need extra help and shows whether current services are effective. For example, Texas Tech University’s Raider Success Hub (providing academic, financial, and mental health support) contributed to record graduation rates—51% in four years and 69% in six years, marking significant improvements over the past decade.
Student and Alumni Surveys
Not all aspects of success can be measured with numbers. Surveys provide insight into:
- Student satisfaction
- Sense of belonging and engagement
- Alumni perspectives on how well the institution prepared them for life after graduation
Collecting this kind of qualitative feedback helps institutions identify gaps and create more personalized learning experiences. By implementing regular surveys—such as gathering student opinions on interactive tools—colleges can build a strong feedback loop. In fact, well-structured feedback processes have been shown to increase student satisfaction by up to 30%.
Measuring Student Success in Today’s World
The main goal of student success—helping learners achieve their academic and personal goals—remains the same. However, the ways it is measured and supported must continue to adapt as student needs and challenges evolve. Today’s students, particularly first-year learners, face challenges that differ greatly from those of the past. For instance, many struggle academically because traditional teaching methods do not always match their learning preferences. This shows that student concerns can have long-lasting effects on their overall college experience.
Here are some of the key factors shaping success today:
Mental and Holistic Well-Being
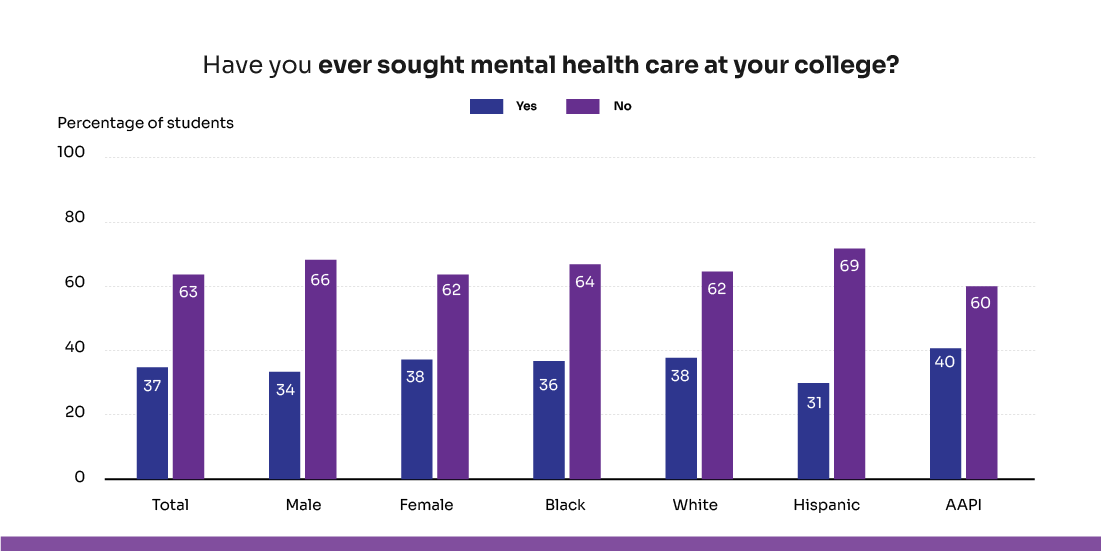
Student well-being is a major predictor of academic performance. Nearly 90% of students report that their mental health has disrupted their studies at least occasionally, with about 10% experiencing daily challenges. Despite this, only 37% seek help, often due to past negative experiences, doubts about effectiveness, social stigma, cost, or uncertainty about how to access resources. Supporting mental and emotional health is therefore essential for student success.
Support for Nontraditional Students
Nontraditional learners—such as students over 23, veterans, and parents—now represent a significant share of the student body. They bring unique challenges and require flexible support systems. More than 73% of higher education enrollments are now nontraditional students. In fact, among applicants over age 23, applications have risen 223% from 2016 to 2024.
Focus on Career Readiness
Students today prioritize career preparation and employability over institutional prestige. They look for programs that offer internships, hands-on training, and clear career pathways. A survey by Wiley found that 57% of students choose their major based on personal interest, 46% on career opportunities, and 41% on the ability to make a positive impact. This shift shows that modern students value practical outcomes alongside academic learning.
Tips to Improve Student Success in Higher Education
Student success is not just about offering a great campus—it’s about making sure students have the right support to achieve their goals. Here are some practical ways institutions can create a stronger and more supportive environment:
Get to Know Your Students
Students do better when they feel recognized as individuals. At larger institutions, it’s easy for them to feel overlooked. Collect background details during enrollment, such as their strengths and possible challenges, and use this information to personalize support. Admissions teams can ask thoughtful questions and track information in a CRM to provide ongoing help. This matters because over 45% of college students report struggling with mental health, which contributes to degree incompletion rates as high as 39%.
Match Students with the Right Resources
Every student has different needs, so offering a variety of resources is key:
- Financial – tuition support, scholarships, and loan guidance
- Academic – tutoring and advising for coursework challenges
- Social – clubs and events to build connections
- Mental – counseling and stress management support
- Physical – access to healthy food, fitness, and wellness activities
Even if a student uses just one of these, having a broad set of resources ensures no one is left behind. Financial pressure is a major factor, with 59% of students considering dropping out and 78% reporting mental health struggles linked to money stress.
Support Students Throughout Their Journey
Support shouldn’t stop after the first year—it needs to continue all the way to graduation. Consistent advising, mentoring, and progress monitoring help institutions step in early when challenges arise. At Penn State, students who had an advising appointment in fall 2023 were 93.6% more likely to return in spring 2024, compared to only 73.9% of students without one .
Encourage a Growth Mindset
Help students see challenges as opportunities for growth rather than setbacks. Many struggle with required courses outside their chosen field, but these classes build transferable skills and career readiness. Encouraging this perspective improves motivation and engagement. Still, only 24% of students use career centers, and 47% say they lack confidence in securing a job after graduation. This highlights the need for both mindset training and practical career preparation.
Promote Early Engagement and Active Learning
Encourage students to engage early through group projects, student organizations, internships, and active learning. Early involvement builds confidence, skills, and a sense of belonging, which improves persistence and outcomes.
- At the University of Houston, students involved in four or more campus activities had an average GPA of 3.3, compared to 2.7 for those with no engagement.
- Research also shows that students in active learning classes score 54% higher on tests and are 1.5 times less likely to fail compared to those in lecture-only courses.
Why Are Success Strategies Important for Students?
Effective success strategies are essential for helping students thrive academically, personally, and professionally. They provide the tools and support needed to improve learning outcomes, increase engagement, and prepare students for life beyond college.
Enhanced Academic Performance
Adopting effective success strategies directly improves academic outcomes. Active learning methods such as group discussions, problem-solving tasks, and interactive lessons help students engage more deeply with their coursework. This boosts participation, confidence, and the ability to retain and apply knowledge in real-world situations.
Increased Graduation Rates
Student engagement is strongly linked to higher graduation rates. Research shows that learners who actively participate in their education are 1.5 times more likely to graduate from high school and 2.5 times more likely to earn a college degree, highlighting the importance of consistent involvement in academic activities.
Improved Retention and Engagement
Personalized support and engaging learning environments keep students motivated and reduce dropout rates. Studies show that students with access to high-quality instruction are 15% more likely to finish high school and 30% more likely to complete college, demonstrating the impact of effective strategies on retention and overall engagement.
Better Mental Health and Well-Being
Prioritizing mental health is essential for overall student success. Programs that emphasize well-being help students manage stress, stay motivated, and achieve both academic and life goals. For example, a program at the Government Engineering College in Buxar highlighted the strong link between mental health and academic performance.
Enhanced Career Readiness
Modern students value practical skills and career preparation over institutional prestige. A survey found that 80% of British teenagers see a university degree as important for success, even though 75% aspire to start their own business. Success strategies that incorporate career guidance, internships, and skill-building help students transition smoothly into the workforce.
Read more: The Ultimate Student Resume Checklist: Key Elements & Benefits for College Admissions
Conclusion
Understanding student success goes beyond just grades—it also includes personal growth, social involvement, and career preparation. By implementing strategies such as early engagement, active learning, strong support systems, and holistic development programs, institutions can boost retention and help students thrive both academically and personally. Focusing on these areas not only improves academic performance but also ensures higher retention and prepares students for long-term success.










No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
Leave a Comment