Wondering how to see how many credits you have? From estimating credits by completed classes to checking official transcripts and using online portals, there are multiple ways to track your progress. Knowing your credit count not only helps you stay on top of degree requirements but also makes transferring schools or planning future courses much easier.
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Did you know that over 40 million Americans have some college credits but no degree? One major reason is confusion around credit requirements. According to an Ellucian survey, more than three-fourths of students who dropped out admitted they didn’t understand what credits they still needed, and only 15% felt confident about transferring their credits to another school. Learning how to see how many credits you have is crucial, because millions of earned credits are sitting unused instead of helping students graduate.
Why It’s Important to Know Your College Credits
College credits are more than just numbers on a transcript — they are the foundation of your degree. Every course you complete contributes toward your graduation requirements, and understanding how these credits add up can save you valuable time and money. Here are five key reasons why keeping track of your college credits is so important:
Staying on Track for Graduation
A standard bachelor’s degree in the U.S. typically requires 120–130 credit hours. By keeping track of your earned credits, you can ensure you’re progressing at the right pace and avoid unexpected delays in completing your degree.
Saving Time and Money with Prior Learning
Students who earn credits through prior learning—such as professional experience or certifications—can save between $1,500 and $10,200 and shorten their bachelor’s degree by an average of seven months. Knowing your credit count makes it easier to identify opportunities like this.
Meeting Prerequisites Efficiently
Many advanced courses require specific prerequisite credits. Being aware of how many credits you’ve completed allows you to plan your course schedule strategically, ensuring you meet requirements and qualify for higher-level classes without unnecessary delays.
Simplifying Credit Transfers
Transferring schools is easier when you know exactly how many credits you’ve earned and which will likely transfer. Only 15% of students feel confident navigating credit transfers, making proper tracking essential. EDMO offers a complete credit transfer evaluation in under 4 hours, helping you quickly understand how your credits apply at a new institution. This fast, reliable process saves time and ensures a smoother transfer experience.
Supporting Financial Aid & Loan Management
Financial aid eligibility often depends on maintaining a minimum number of credit hours each term. Falling short could affect your scholarships, grants, or loan qualifications. On average, each credit hour at a U.S. public four-year university costs about $406 for tuition alone, and approximately $933 when room and board are included. Tracking your credits helps you maximize financial aid while minimizing unnecessary costs.
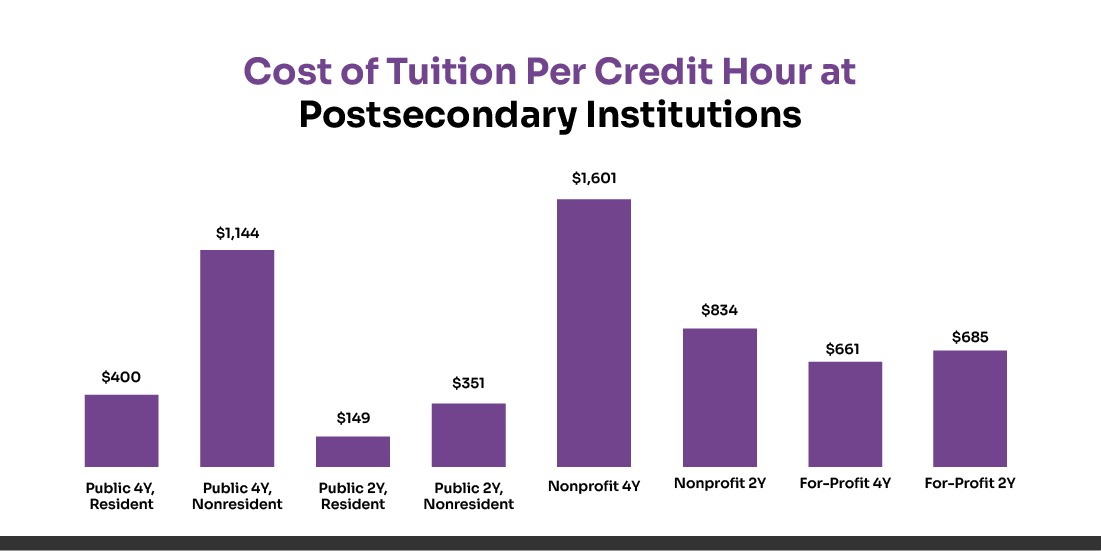
How to Determine How Many College Credits You Have
Understanding your earned credits is essential for tracking academic progress, planning upcoming courses, or transferring to another institution. If you’ve ever wondered how to see how many credits you have, here are the best ways to find out:
Estimate Credits Based on Completed Classes
A simple way to get a rough estimate is by multiplying the number of courses you’ve completed by three, since most U.S. college classes are worth three semester credit hours. This usually equals about 45–48 contact hours per semester. Keep in mind, though, that not all courses carry the same weight—some may be worth more or fewer credits—so this method provides only an approximation.
Check Your Official Records
For the most accurate count, reach out to your school’s registrar or academic advisor. They can provide a detailed summary of credits earned, those currently in progress, and the requirements still remaining.
Use Online Academic Portals (for Current Students)
Many colleges now offer online portals to help students track progress. For example, Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU) provides a program evaluation tool that shows completed credits, in-progress classes, and degree requirements still outstanding.
Request Transcripts (for Former Students)
If you’re no longer enrolled, the best way to confirm your credit history is to request an official transcript from your previous institution(s). This is especially important if you plan to transfer credits. In fact, transfer enrollment is growing steadily—13.1% of continuing undergraduates in Fall 2024 were transfer students, up from 11.9% in 2020.
Consider Special Credits
Not all credits come from standard courses. Many students earn credits through Advanced Placement (AP) exams, International Baccalaureate (IB) courses, or dual enrollment programs. AP courses alone can earn anywhere between 3 and 8 credits, depending on your exam score and the institution’s policy.
Knowing how to see how many credits you have ensures you understand how close you are to finishing your degree, prevents unnecessary course retakes, and makes transferring to another school a much smoother process.
How Does Credit Transfer Work?
Transferring college credits allows you to bring the work you’ve already completed to a new school, potentially saving time and money. Here’s a simple guide to understanding how the process works:
Choose a Transfer-Friendly School
Look for colleges or universities that have clear transfer policies and accept previously earned credits. Each institution may have different rules about which credits can transfer and how they apply toward your program.
Submit Your Transcripts
Request official transcripts from all the schools you’ve attended. These documents are necessary for the new school to evaluate your credits.
Credit Evaluation
Once your transcripts are received, the school’s transfer evaluation team will review them to determine which credits can be accepted and how they fit into your program.
Factors Considered for Transfer
During the evaluation, four main factors are considered:
Accreditation: Credits must come from nationally or regionally accredited institutions.
Grades: Typically, courses must have a minimum grade (e.g., C- or higher) to transfer.
Course Alignment: The content of your previous courses is compared with the new school’s curriculum to see how they fit—toward major requirements, general education, or electives.
Time: While credits generally don’t expire, some fields, like IT or healthcare, may require recent coursework to fulfill major-specific requirements.
Outcome of Transfer: Accepted credits may count toward your major, general education, or as elective credits. Even if a course doesn’t match your new program, it can often be applied as a free elective, ensuring your prior work still contributes to your degree.
With the EDMO plugin, universities can automate transcript evaluation and document verification, making the credit transfer process faster and more accurate. It helps institutions streamline data collection and comparison, reducing manual effort and improving student satisfaction.
By understanding these steps, you can make the credit transfer process smoother and ensure your previous academic efforts are recognized.
Common Mistakes Students Make About College Credits
Understanding how college credits work is essential for graduating on time and avoiding unnecessary costs. However, many students make critical errors when it comes to managing their credits. Here are some of the most common mistakes to watch out for:
Assuming All Courses Are Worth the Same Credits
Many students believe every course is worth three credits, but that isn’t always true. Labs, seminars, and intensive courses can vary in credit value. Data shows that full-time students take under 27 credits per year but earn fewer than 22 credits, falling short of the 30 credits needed annually to graduate on time. Only 28% of students actually reach that benchmark
Believing All Credits Will Transfer
Transferring schools doesn’t mean all your credits will come with you. About 40% of students try to transfer credits, but over half lose some in the process, and 1 in 5 have to retake classes. A 2024 study also showed that students lose an average of 43% of their credits—almost a semester’s worth when moving to a new school.
Ignoring General Education Requirements
Some students focus solely on their major and overlook general education credits. This oversight often surfaces during academic audits, where students discover gaps that must be filled before graduation.
Not Tracking Credits Regularly
Relying on rough estimates instead of verified records is a common mistake. Without accurate tracking, students may misunderstand their progress. Research shows that 25% of students transferred few or none of their credits, and 37% reported the process as difficult.
Repeating Courses Already Passed
Transfer challenges often cause students to lose credit recognition, even for classes they’ve successfully passed. As a result, about 20% of students are forced to retake courses they’ve already completed. This not only delays their academic progress but also leads to unnecessary expenses in tuition and fees—costs that could have been avoided with clearer credit evaluations and better transfer planning.
Assuming Credits Never Expire
While credits technically don’t expire, their relevance can diminish over time. For example, older credits in fast-changing fields like IT may only transfer as electives, rather than fulfilling major requirements.
Tips to Keep Track of Your College Credits
Staying on top of your college credits is one of the best ways to graduate on time and avoid unnecessary delays. Here are some practical tips to help you stay organized and on track:
Use Your School’s Online Portal
Most colleges provide online platforms where you can see your completed, in-progress, and remaining credits. Checking this regularly keeps you updated. For example, SUNY’s ASAP program, which emphasizes proactive tracking, improved credit completion rates by 20%. About 50% of ASAP students were on track to graduate on time, compared to only 18% of non-ASAP students.
Meet With Your Academic Advisor
Advisors can explain how your credits fit into degree requirements and help you plan future courses. Yet, only 55% of students say they get guidance on required coursework, and just 52% receive help tracking degree progress. Meeting with your advisor regularly can keep you from falling behind.
Request and Review Transcripts
Requesting unofficial transcripts each semester gives you a clear picture of what credits you’ve earned. This helps prevent confusion and ensures you’re accurately tracking your progress.
Create a Personal Credit Tracker
Keep a simple spreadsheet or planner with your course names, grades, and credit values. This personal record is especially useful if you transfer schools. Remember, students on average earn only 76% of the credits they attempt, meaning 1 in 4 credits don’t count because of failed or incomplete classes.
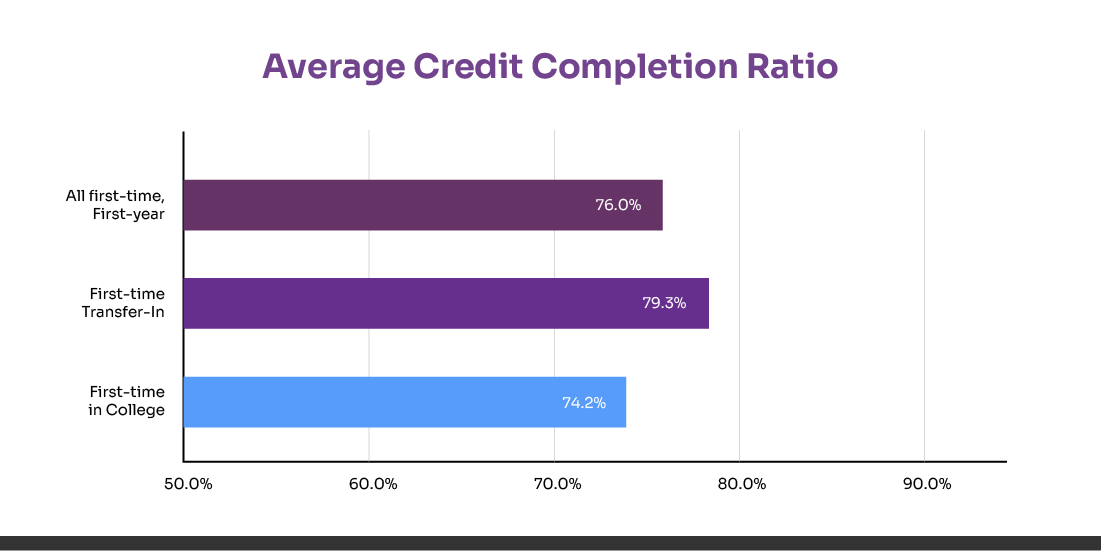
Understand Degree Requirements Early
Know how many credits your program requires for general education, electives, and your major. Not enrolling in enough credits per semester is a common reason students fall behind. Research shows that students who don’t take at least 15 credits per semester are far less likely to graduate on time.
Check Transfer Policies Before Moving Schools
If you’re planning to transfer, look at the school’s credit transfer rules ahead of time. This can save you from losing credits or having to repeat courses unnecessarily.
Review Credits Every Semester
At the end of each semester, compare your earned credits with your graduation plan. Catching gaps early makes it easier to adjust. Still, only 51% of full-time students earn 24 or more credits in their first year—a key milestone for staying on track.
Conclusion
Keeping track of your college credits is one of the smartest ways to stay on the path to graduation without wasting time or money. By using your school’s online portal, meeting with advisors, reviewing transcripts, and maintaining a personal tracker, you can avoid delays and make sure every class counts toward your degree. Whether you’re a current student or planning a transfer, knowing how to see how many credits you have will give you control over your academic journey and help you reach your degree goals on time.










No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
Leave a Comment