Table Of Contents
- 1Introduction
- 2What Is a Data Management Platform for Higher Education?
- 3Key Components of a Higher Education Data Management Platform
- 4Data Integration and Analytics Layer
- 5Why a Higher Education Data Management Platform Matters
- 6Benefits of Effective Data Collection and Management
- 7Key Challenges in Implementing Data Management in Higher Education
- 8Key Principles of Education Data Management for Schools and Trusts
- 9Types of Data Management in Higher Education
- 10How Higher Education Data Management Platforms Work
- 11Best Practices for Effective Data Management in Higher Education
- 12Tools and Technologies to Streamline Data Management
- 13Challenges of Managing Education Data in Schools
- 14Conclusion
Introduction
Data management in higher education plays a crucial role in how colleges and universities operate, plan, and support student success. Institutions generate large volumes of data across admissions, academics, finance, and student services, often spread across disconnected systems. Without a structured approach, this data can become difficult to manage, analyze, and trust.
By adopting the right tools and best practices, higher education institutions can support student success, streamline operations, and make informed, data-driven decisions.
What Is a Data Management Platform for Higher Education?
A data management platform for higher education is a centralized system that helps colleges and universities collect, organize, validate, and analyze data from across the institution. It brings together information from multiple departments and systems into one secure, unified environment, allowing institutions to make informed, data-driven decisions.
Higher education institutions typically manage data across many disconnected systems, such as admissions, academics, finance, and student services. A data management platform connects all these systems so information is organized, accurate, and easy to understand.
Key Components of a Higher Education Data Management Platform
A higher education data management platform is made up of several core systems that work together to collect, organize, and analyze institutional data. Each component plays a specific role in supporting academic operations, student success, and decision-making.
Student Information System (SIS)
A Student Information System (SIS) is the central system of record for student data. It stores and standardizes information related to admissions, enrollment, grades, attendance, and personal details. The SIS supports daily institutional operations and student services by ensuring data consistency and reliability.
Learning Management System (LMS)
A Learning Management System (LMS) represents the instructional layer of campus technology. It supports data management in higher education by managing course content, assignments, assessments, and communication between students and faculty. While the SIS handles administrative records, the LMS captures academic engagement and learning activity.
Data Integration and Analytics Layer
The data integration and analytics layer sits above systems like the SIS and LMS, bringing their data together and transforming it into meaningful insights. This layer strengthens data management in higher education by enabling institutions to:
- Monitor student performance and engagement
- Identify at-risk students early
- Track enrollment and retention trends
- Support strategic planning and reporting
Why a Higher Education Data Management Platform Matters
Higher education institutions handle vast amounts of student, academic, and operational information across multiple systems. An effective educational data management platform centralizes this data, improving accuracy, strengthening governance, and ensuring timely access to reliable information for better decision-making.
| Key Benefit | What It Enables | Example Metrics | Primary Stakeholders |
| Improved Student Outcomes | Identifies at-risk students early and enables timely interventions to improve retention, progression, and graduation rates | Retention rate, graduation rate, course completion rate, academic probation rate, student engagement indicators | Student success teams, academic advisors, faculty, enrollment management |
| Streamlined Operations | Reduces data silos, automates manual processes, and minimizes duplication of effort across departments | Time spent on manual data tasks, process cycle time, staff productivity, and operational cost savings | Administrative leadership, IT teams, institutional research, department heads |
| Data-Driven Decision-Making | Provides access to accurate, real-time, and unified data that supports faster and more confident institutional decisions | Decision turnaround time, forecast accuracy, enrollment yield, resource allocation effectiveness | Presidents, provosts, deans, cabinet leaders, institutional research |
| Simplified Reporting & Compliance | Centralizes governed data to speed up reporting, reduce errors, and ensure timely compliance with regulatory requirements | Report preparation time, number of data reconciliations, reporting accuracy, compliance timelines | Institutional research, compliance officers, finance teams, enrollment reporting units |
By enabling meaningful analytics and reporting, these platforms help institutions improve student success, streamline operations, support informed decision-making, and meet regulatory requirements more efficiently.
Benefits of Effective Data Collection and Management
Effective data collection and management enable educational institutions to make informed decisions that directly improve student success, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
Track Student Progress
Data management systems help educators track student progress by monitoring academic performance and behavioral patterns over time. These systems quickly highlight early warning signs, such as declining grades in specific subjects or increasing absenteeism among student groups. With timely insights, institutions can intervene early through tutoring, academic counseling, or parent engagement before challenges escalate. Data-driven tracking also supports personalized learning by helping educators tailor support for struggling students while providing advanced opportunities for high performers. However, only 27% of institutions report having highly effective tools to identify at-risk students, with many still relying on outdated or manual processes.
Optimize Resource Allocation
Data management systems help institutions optimize resource allocation by replacing assumptions with accurate, data-driven insights. This is particularly important in areas such as GAG pooling, where reliable data supports fair and efficient distribution of funds. By understanding exactly where gaps exist, schools can allocate budgets more strategically, such as investing in learning materials for underperforming subjects, strengthening student support services, or expanding high-impact extracurricular programs.
Improve Teaching Outcomes
Data-driven insights help educators refine their teaching methods and curriculum. When data shows students struggling with certain concepts—like fractions in math teachers can adjust lessons, provide extra practice, or use alternative resources. By analyzing assessment results and classroom metrics, educators can see which strategies work best.
Ensure Compliance with Standards
Educational institutions must follow strict academic, financial, and reporting regulations. Data management systems make compliance easier by securely organizing records like attendance, grades, and financial data. When audits or inspections occur, institutions can quickly generate accurate reports without manual effort. This reduces administrative workload and lowers the risk of errors or non-compliance.
Key Challenges in Implementing Data Management in Higher Education
While data management platforms offer significant benefits, higher education institutions often face several challenges during implementation. Addressing these issues requires the right technology, planning, and institutional alignment.
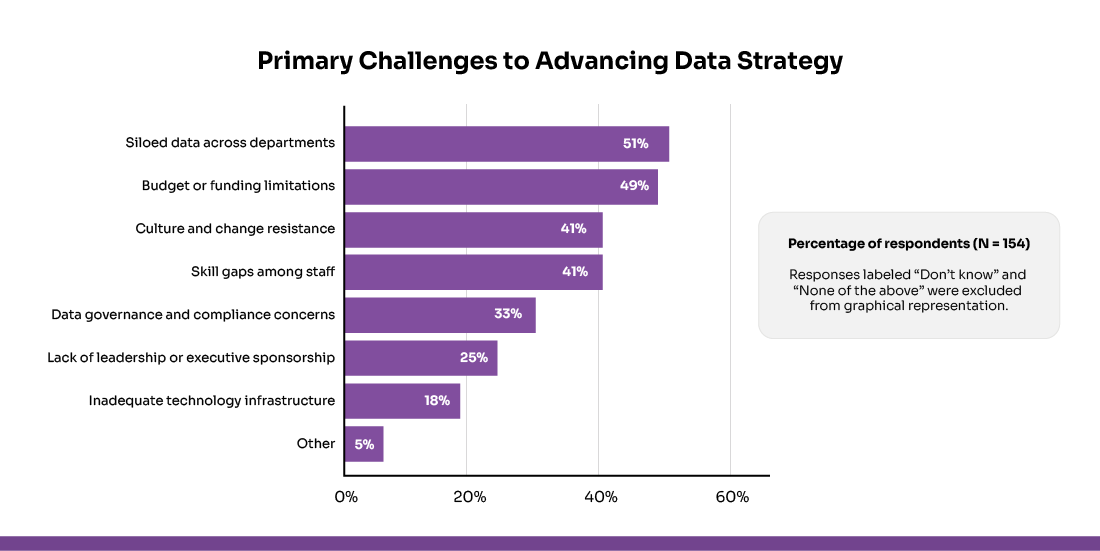
Data Silos Across Systems and Departments
Many colleges and universities use older systems that don’t work well together, leading to disconnected and scattered data. In fact, 51% of institutions reported siloed data across departments as a top barrier to advancing their data strategies. Sometimes, departments are also reluctant to share information, which makes these silos worse. Solving this requires teamwork between departments and tools that combine data from different sources. Connecting all systems gives a complete and accurate view of students and operations.
Data Quality and Consistency Issues
Poor data like incomplete, outdated, or inconsistent records—can make reports and analysis unreliable. To fix this, schools need clear rules and practices for managing data. Regularly checking, cleaning, and standardizing information helps keep it accurate and consistent. This ensures that decisions are based on trustworthy data.
High Implementation and Maintenance Costs
Setting up a full data management platform can be expensive, especially for smaller colleges and universities. A survey of higher education IT leaders found that 44% of institutions report high costs for maintaining on-premises systems, which can limit funds for innovation and student services. These costs include both initial setup and ongoing maintenance. As a result, careful planning and budgeting are essential to ensure the platform delivers value.
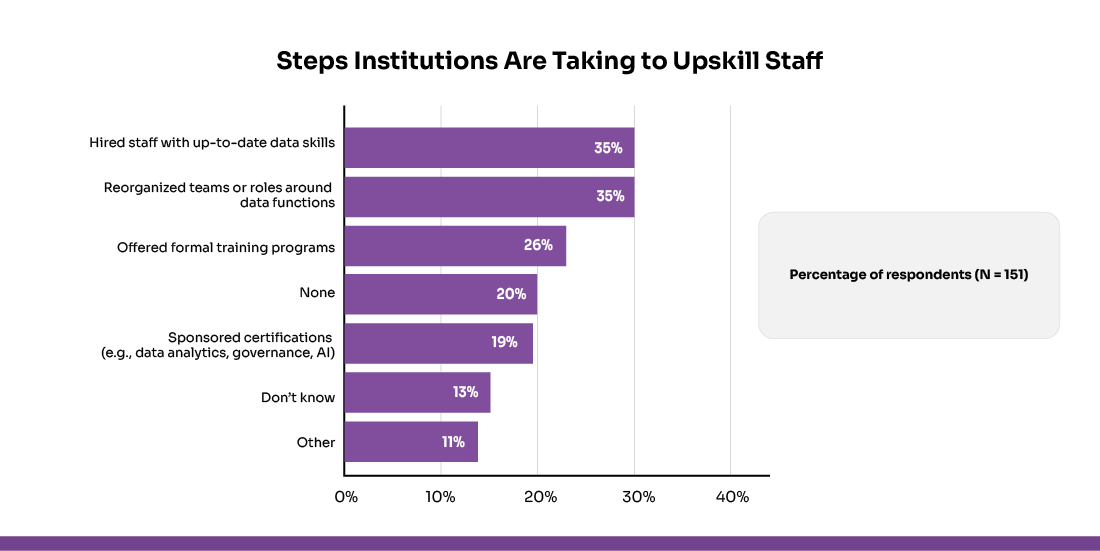
Limited Staff Adoption and Training Gaps
The success of a data management platform depends on staff engagement and adoption. Without proper training and clear communication of benefits, resistance to change can slow implementation. Institutions should provide structured training programs and show how better data access supports daily tasks and decision-making. In fact, 20% of respondents reported that their institution has taken no steps to upskill staff for data modernization efforts.
Security, Privacy, and Compliance Risks
Colleges and universities manage sensitive student and financial data, making security a top concern. Choosing a platform with strong encryption, role-based access, and built-in governance helps protect this information. Compliance support ensures institutions follow regulations like FERPA or GDPR. These measures reduce the risk of data breaches and maintain trust with students, staff, and regulators. Strong security practices are essential for safe and responsible data management.
Key Principles of Education Data Management for Schools and Trusts
Effective education data management ensures accurate decision-making, protects sensitive information, and supports better outcomes for students and staff. Schools and trusts that follow these core principles can build a reliable and secure data environment.
Accuracy
Accuracy is essential for reliable education data. Correct records such as attendance, grades, and assessments—help prevent errors in funding, student support, and reporting. Even small mistakes, like wrong attendance or test scores, can lead to misclassification or missed interventions. In fact, 32% of U.S. colleges report discrepancies in applicant data, affecting admissions and support planning. Schools can improve accuracy through clear data entry guidelines, staff training, automated validation tools, and regular audits.
Consistency
Consistent data formats and definitions ensure information flows smoothly across systems and departments. Without standardization—like uniform labels for grades or assessments—data integration can become unreliable. While 92% of U.S. higher education institutions are modernizing their data systems, only about 1% consider them fully modernized, often due to inconsistent data practices. Using centralized systems and agreed-upon standards helps ensure data is accurate and comparable. Consistency improves reporting, collaboration, and decision-making across the institution.
Security
Educational data includes sensitive information about students, staff, and finances, which must be protected from cyber threats and unauthorized access. Strong security measures like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular system updates help keep data safe. Routine security assessments allow schools to identify and fix vulnerabilities early. In fact, about 60% of UK secondary schools experienced a cyber-attack or data breach in the past year, far higher than many other sectors. Robust security practices are essential to protect data and maintain trust.
Accessibility
Data is most valuable when it is accessible to the right people at the right time. Teachers, administrators, and counselors rely on timely access to accurate data to support students and make informed decisions. User-friendly systems with role-based access ensure that staff can quickly retrieve relevant information without being overwhelmed or exposed to unnecessary data. This balance improves efficiency while maintaining control over sensitive records.
Privacy and Regulatory Compliance
Schools and trusts must comply with data protection regulations such as FERPA in the United States and GDPR in Europe. These regulations govern how student and staff data is collected, stored, and shared. For example, FERPA requires parental consent before student records are disclosed to third parties. Strong privacy practices reduce legal risk and reinforce institutional accountability.
Types of Data Management in Higher Education
Effective data management plays a critical role in shaping an institution’s planning, operations, and decision-making processes. When implemented correctly, it streamlines complex workflows, improves data accuracy, and allows staff to focus on higher-value academic and administrative work. Below are the key types of data management commonly used in higher education institutions:
Data Preparation
Data preparation involves cleaning, validating, and transforming raw data into a format suitable for analysis. This process may include correcting errors, standardizing formats, or merging multiple data sets. It is especially important for institutions managing large volumes of student, faculty, and operational data.
Data Pipelines
Data pipelines automate the movement of data between different systems and applications. They ensure that information is transferred consistently and updated in real time or at scheduled intervals. For colleges and universities that rely on multiple platforms, data pipelines help maintain data accuracy and reduce manual effort.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load)
ETL processes enable institutions to extract data from various source systems, transform it into a usable format, and load it into a target system such as a data warehouse. This approach supports reporting, analytics, and cross-system data consistency across departments.
Data Catalogs
Data catalogs help institutions manage and organize metadata by providing a centralized view of available data assets. They make it easier to locate datasets, understand data quality, and track changes over time. This improves transparency and supports better data discovery across teams.
Data Warehouses
Data warehouses serve as centralized repositories that consolidate data from multiple sources. They enable institutions to store structured data in one place, making analysis, reporting, and trend identification more efficient and reliable.
Data Governance
Data governance establishes the policies, standards, and procedures for managing institutional data. It ensures data accuracy, compliance, accountability, and secure handling of sensitive student and academic information across systems.
Data Architecture
Data architecture defines how data is structured, stored, and accessed across the institution. It provides a strategic framework for organizing data flows and ensures that different departments can easily access consistent and reliable information.
Data Security
Data security focuses on protecting sensitive institutional data from unauthorized access, breaches, or cyber threats. It includes measures such as access controls, encryption, and monitoring to safeguard student, financial, and academic records.
Data Modeling
Data modeling involves designing and documenting how data elements relate to one another. Often supported by specialized tools or external services, it helps institutions improve data consistency, integration, and long-term scalability.
How Higher Education Data Management Platforms Work
A data management platform in higher education helps colleges and universities organize, secure, and make sense of their data to support better decisions and student outcomes. Here’s how it works:
Integrates Institutional Data
The platform brings together information from different departments and systems into a single, centralized location. This eliminates silos, making it easier to access comprehensive student, faculty, and operational data.
Establishes Data Governance
It ensures that all data is accurate, consistent, and compliant with regulations such as FERPA. Policies, standards, and validation processes built into the platform help maintain high-quality data.
Provides Analytics and Reporting
The platform transforms raw data into actionable insights using dashboards, predictive analytics, and custom reports. This enables administrators and educators to track trends, forecast outcomes, and make informed decisions quickly.

Best Practices for Effective Data Management in Higher Education
Implementing a strong data management strategy in colleges and universities requires clear policies, skilled staff, and secure, actionable systems. By adopting the right education data management solutions, institutions can ensure data accuracy, improve system adoption, and support informed, data-driven decision-making across departments.
Establish a Data Governance Framework
Define roles, responsibilities, and policies for managing data across the institution. A clear governance structure ensures accountability and a defined chain of command for all data-related decisions.
Prioritize Data Quality
Regularly validate and clean data to maintain accuracy and reliability. High-quality data is the foundation for effective reporting, analytics, and informed decision-making.
Train and Engage Staff
Providing proper training helps staff use data management systems effectively and confidently. Without training, staff may struggle to adopt new systems or fully utilize analytics tools. Research shows that only about one‑third of schools report having enough staff for data-related tasks, highlighting a widespread skills gap. Structured training programs and ongoing support help institutions build staff capacity.
Leverage Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics
Use analytics tools to generate actionable insights, from identifying at-risk students to guiding budget and resource planning. Predictive and prescriptive analytics enable proactive and data-driven decision-making.
Enforce Security and Role-Based Access
Choose a platform with robust security features, including role-based permissions, so that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data. This protects privacy and ensures compliance with regulations such as FERPA.
Tools and Technologies to Streamline Data Management
Effective data management in educational institutions depends on the right mix of tools and technologies. The following systems help schools and universities centralize information, improve efficiency, and support data-driven decision-making.
Student Information Systems (SIS)
Student Information Systems (SIS) such as PowerSchool and Skyward play a key role in managing student data efficiently. These platforms centralize essential information, including grades, attendance records, and contact details, reducing manual work and simplifying administrative processes.
Data Analytics Tools
Data analytics platforms like Tableau and Microsoft Power BI enable institutions to analyze large volumes of data and identify meaningful trends. Schools can use these tools to detect performance gaps, such as declining scores in specific subjects or rising absenteeism in certain grades. Their visual dashboards make insights easy to understand and share across teams.
Learning Management Systems (LMS)
Learning Management Systems (LMS), including Moodle and Google Classroom, support academic tracking and instructional planning. These platforms allow educators to assign coursework, evaluate student performance, and communicate with learners in a single, integrated environment, improving both teaching efficiency and student engagement.
Cloud Storage Solutions
Cloud-based storage platforms such as Google Drive and Microsoft Azure offer secure and scalable access to institutional data. These solutions allow authorized users to store, access, and collaborate on information from anywhere, supporting flexibility and continuity in data management. Cloud storage also reduces dependence on on-premise infrastructure while improving system reliability. Recent reports show that 88% of higher education institutions have moved at least a quarter of their applications to the cloud, with 79% stating that cloud adoption has met or exceeded expectations.
Challenges of Managing Education Data in Schools
Managing education data in schools and trusts can be complex, and institutions often face several key challenges. Addressing these issues proactively ensures that data systems are effective, secure, and widely adopted.
Lack of Staff Training
Limited staff training is a major challenge in effective data management. Teachers, administrators, and support teams may not have the skills needed to enter, analyze, or interpret data correctly. This can lead to data errors, low system adoption, and frustration among users. Schools should invest in continuous training through workshops, online learning, or expert-led sessions as systems evolve. A 2025 survey of U.S. K-12 ed-tech leaders found that 17% had never received training on student data privacy, despite its high priority.
Challenges in Selecting the Right Tools
Selecting the wrong data management tools can create inefficiencies, integration issues, and higher costs. Schools must first evaluate their specific needs before choosing a platform. Important factors include scalability, usability, system compatibility, customization, and open API availability. Although nearly 90% of schools use multiple third-party tools to handle student data, many lack proper policies to manage them securely. Conducting demos, trials, and thorough evaluations helps institutions choose tools that support both current and future requirements.
Resistance to Change
Staff may be hesitant to adopt new data management systems, especially if they are accustomed to traditional workflows or unfamiliar with digital tools. Clear and consistent communication about the benefits of the system, such as simplifying tasks, improving efficiency, and enhancing student outcomes, can help reduce resistance. Involving staff in decision-making, offering feedback channels, hosting Q&A sessions, and implementing change management strategies like pilot programs or tech “change ambassadors” can further increase buy-in and ease the transition.
Ensuring Data Privacy and Security
Educational institutions handle sensitive student, staff, and family information, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. Data breaches can cause legal issues, reputational damage, and financial losses. Schools should implement strong security measures such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular system audits.
Conclusion
Effective data management in higher education is no longer optional, it is essential for improving student outcomes, strengthening institutional operations, and enabling informed decision-making. By centralizing data, establishing strong governance, investing in staff training, and adopting secure, scalable technologies, colleges and universities can turn fragmented information into meaningful insights. With the right data management approach, institutions are better equipped to adapt to change, meet compliance requirements, and support long-term academic and operational success.










No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
Leave a Comment