Table Of Contents
Introduction
Student engagement plays a vital role in higher education, shaping academic success, retention, and overall satisfaction from the moment students begin their enrollment journey. When students are actively involved in learning, they develop a deeper understanding, stronger critical thinking skills, and a greater sense of ownership over their education. However, fostering this level of involvement requires intentional approaches that go beyond traditional lectures and passive learning methods.
In this blog, we explore effective engagement strategies for higher education institutions, highlighting how AI-powered tools, collaborative learning, and technology integration can help students stay motivated, connected, and successful throughout their academic journey.
What Is Student Engagement?
Student engagement refers to the level of participation, attention, curiosity, interest, and motivation a student demonstrates throughout their academic journey, starting from enrollment. It reflects not only a student’s effort but also how connected and involved they feel with the institution, courses, and learning community.
Increasing engagement goes beyond a student’s personal willpower. Instructors, administrators, and other faculty play a critical role in fostering meaningful engagement. They must create a supportive, stimulating environment and model engagement themselves, helping to establish a positive classroom culture that encourages students to stay motivated.
Effective engagement is not just about keeping students focused. It is about providing value through their interactions with peers, teachers, the curriculum, and the wider learning community, ensuring that students feel connected, supported, and inspired to learn.
Understanding the Different Types of Student Engagement
Student engagement is influenced by many factors in a student’s life, including their learning experiences, emotional and mental well-being, physical health, financial situation, and outside responsibilities. In the classroom, engagement can be divided into three main types:
Cognitive Engagement
Cognitive engagement refers to the mental effort students put into understanding complex ideas and concepts. It includes activities like asking questions for clarification, analyzing information, and using strategies to learn effectively. This type of engagement shows how actively students are thinking and processing the material.
Emotional Engagement
Emotional engagement involves students’ feelings and attitudes toward learning. When students feel interested, excited, or motivated by classroom activities, they are more likely to invest time and energy in their work. Positive emotions help sustain focus and encourage deeper involvement.
Behavioral Engagement
Behavioral engagement is about the actions students take in response to learning. This includes attending classes, participating in discussions, taking notes, completing assignments, and other visible forms of involvement. Active participation reflects a student’s commitment to their education.
Importance of Student Engagement in Higher Education
Student engagement refers to the level of interest, participation, and involvement students show in their learning activities. High levels of engagement help students succeed academically while enabling institutions to improve retention, performance, and overall educational quality. Below are the key reasons why engagement is essential in higher education.
Enhances Academic Performance and Learning Outcomes
Engaged students actively participate in classes, discussions, and hands-on activities, which leads to a better understanding of concepts. This active involvement improves critical thinking, knowledge retention, and overall academic performance.
Reduces Student Dropout and Improves Retention
Strong student engagement plays a critical role in reducing dropout rates and improving retention. When students feel connected to their coursework, peers, and faculty, their motivation increases, making them more likely to remain enrolled and complete their programs on time. Evidence from Academic Year 2024 shows that undergraduate students employed by the Division of Student Affairs achieved notable academic success. Among 974 students, the average GPA was 3.259, and retention reached an impressive 95%, clearly highlighting the positive impact of sustained and purposeful student involvement.
Supports Institutional Growth and Sustainability
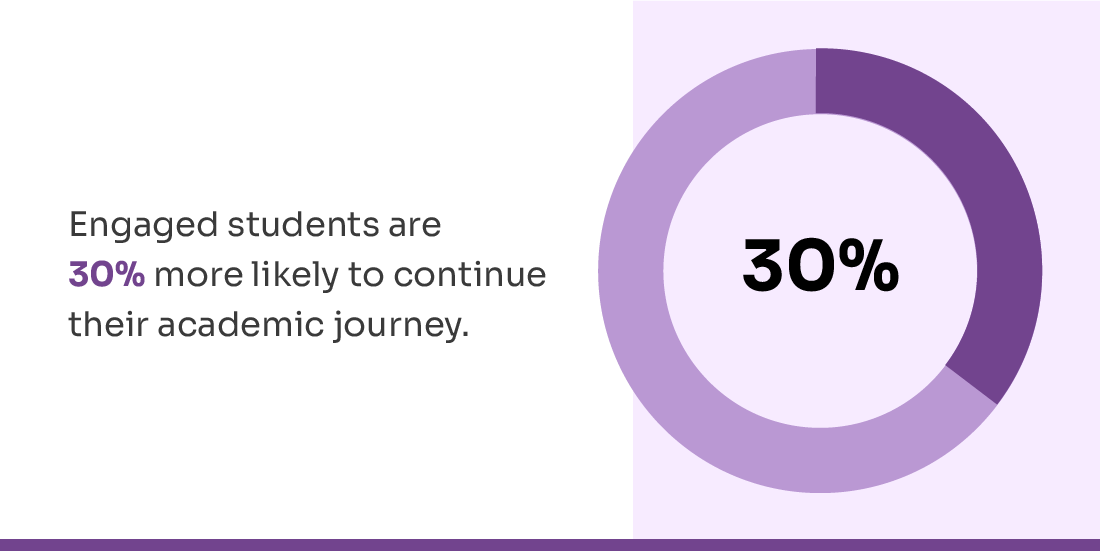
Higher levels of engagement directly contribute to institutional growth and long-term sustainability. When students are actively involved in academic and extracurricular activities, they are significantly more likely to persist in their studies and complete their programs successfully. Research indicates that engaged students are nearly 30% more likely to continue their academic journey, leading to improved retention and graduation rates. These positive outcomes strengthen key institutional performance metrics, enhance reputation, and support financial stability by reducing dropout-related losses and maximizing tuition continuity.
Improves Teaching Effectiveness and Faculty Impact
Data from classroom interactions, assessments, and activities give educators useful insights. By looking at how students participate and respond, teachers can adjust their methods to better support learning. Student Active engagement strategies such as collaborative projects, interactive discussions, and purposeful use of technology have been shown to increase student participation by as much as 50%, resulting in more dynamic classrooms and more effective, impactful teaching experiences.
Encourages Continuous Improvement Through Data Insights
Monitoring engagement provides valuable insights for institutional improvement. By analyzing engagement patterns, universities can enhance academic support services, optimize learning strategies, and create a student-centered educational ecosystem.
16 Effective Student Engagement Strategies in Higher Education
Strategies in higher education focus on creating meaningful learning experiences that encourage students to actively participate in their studies. These approaches use well-designed courses, inclusive teaching methods, and smart use of technology to strengthen connections between students, faculty, and institutions.
Promote Meaningful Discussions and Critical Thinking
Promoting discussion-driven learning helps students feel intellectually valued and actively involved in the learning process. By integrating discussion forums, live debates, reflective writing prompts, and inquiry-based questions, instructors can challenge students to analyze concepts, consider diverse perspectives, and think critically. Providing timely and personalized feedback through text or short video responses strengthens instructor presence and fosters collaborative learning among peers.
Example:
An instructor shares weekly discussion questions on the LMS and responds with short video messages that acknowledge student ideas, encourage discussion, and prompt learners to build on each other’s thoughts.
Utilize Social Media as an Extension of the Classroom
Social media platforms, already embedded in students’ daily routines, can be effectively used to extend learning beyond traditional classroom settings. By sharing relevant academic articles, short videos, expert insights, and real-world examples, instructors can encourage informal learning and ongoing engagement outside scheduled class time. When used thoughtfully and in line with institutional guidelines, social media helps foster discussion, collaboration, and knowledge sharing among students.
Example:
The University of Miami Health System regularly shares educational video content featuring healthcare professionals such as Dr. Ariel Eber, Assistant Professor of Dermatology, to engage learners and the wider academic community. Similarly, an instructor may create a course-specific hashtag on X (formerly Twitter), allowing students to share lecture takeaways, discuss current events related to the subject, and interact with peer-generated content in a structured and meaningful way.
Establish Clear and Accessible Communication Channels
Creating clear, consistent, and accessible communication pathways is key to keeping students engaged. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can quickly answer common questions about assignments, deadlines, or course materials, reducing confusion and building trust. Setting clear expectations for response times, virtual office hours, and discussion participation ensures students know how and when to reach out. Encouraging peer-to-peer communication further strengthens academic communities and promotes collaborative problem-solving.
Example: The University of Hawaiʻi is expanding its use of AI to support students across all 10 campuses, with student-success chatbots set to be launched system-wide by fall 2025 to provide instant guidance and assistance. EDMO’s Student Copilot takes this further by providing an omnichannel, student-facing platform that delivers real-time application updates, resolves queries, and guides learners through each stage of enrollment. By tailoring responses to each student’s profile, progress, and pending tasks, Student Copilot ensures students stay on track, engaged, and supported throughout their academic journey.
Apply Automation and Learning Analytics to Support Student Progress
AI-powered tools and learning analytics help instructors monitor engagement in real time, enabling timely and personalized support. Features such as automated alerts, conditional content release, and progress tracking allow educators to identify early signs of disengagement and provide interventions before challenges escalate. These insights empower instructors to offer tailored feedback, recommend resources, and guide each student based on their individual learning needs.
Example:
At Australian Catholic University (ACU), researchers implemented an AI-based analytics system that analyzed enrollment data to identify students at risk of disengaging or dropping out. The tool accurately flagged at-risk postgraduate students in 17 out of 20 cases, allowing instructors to intervene early.
Acknowledge and Celebrate Student Effort and Achievement
Acknowledging students’ efforts and accomplishments is a powerful way to boost motivation and reinforce the importance of learning. Celebrating both academic performance and creative contributions helps students feel valued, particularly in online or hybrid learning environments where recognition can be limited. Research shows that around 65% of students report that encouragement from instructors significantly increases their motivation, highlighting how meaningful recognition can enhance engagement and drive better outcomes.
Example:
An instructor highlights exemplary discussion contributions or project work during weekly announcements, fostering peer recognition and building a culture of pride and shared achievement
Establish Schoolwide Conditions for Standards-Based Learning
Institutional leaders play a critical role in creating environments where all students can actively engage in rigorous, standards-based learning. Engagement is not driven solely by curriculum design or classroom structures it depends on a culture that prioritizes student well-being, participation, and academic ownership. When schools intentionally cultivate these conditions, students are better prepared to meet learning standards and persist through academic challenges.
Key Conditions for Engagement:
Safe and Supportive Environments:
Students must feel physically, emotionally, and psychologically safe to participate fully. A secure environment encourages students to share ideas, ask questions, and take intellectual risks without fear of judgment.
Conducive Learning Environments:
Classrooms should be designed to promote collaboration, discussion, and critical thinking. This includes thoughtful physical layouts as well as a classroom culture that values curiosity and inquiry.
Support for Student Self-Regulation:
Teaching students how to manage their learning, such as goal-setting, time management, and reflection, helps them stay engaged and make consistent academic progress.
Empowering Learning Environments:
When students feel their voices matter and their contributions are valued, they are more motivated to engage deeply with course content and take responsibility for their learning.
Allocate More Time for Collaborative Active Learning
Lessons are more effective when designed to allow exploration, discussion, and discovery. Rather than explaining all concepts upfront, educators should provide opportunities for students to investigate ideas independently and collaboratively. This approach encourages productive struggle, which strengthens understanding.
Example:
- Passive Learning: A teacher delivers a full lecture on how states chose their capitals, followed by a recall-based assignment.
- Active Learning: A teacher introduces key vocabulary, poses an open-ended question (e.g., “What factors influence the selection of a capital city?”), and allows students to research, discuss, and debate answers collaboratively using provided resources.
This shift transforms students from passive listeners into active problem-solvers.
Empower Students with Meaningful Roles and Responsibilities
Engagement deepens when students are given real ownership over the learning process. Leaders can support teachers in creating classroom structures where students track their progress, support peers, and rely on collaborative problem-solving before seeking teacher intervention. This builds independence and confidence.
Example:
Teachers assign students specific roles within learning teams such as facilitator, evidence checker, or summarizer. A team facilitator may use guiding questions like, “What evidence supports your idea?” Students first practice these roles using non-academic topics before applying them to complex academic tasks.
Enable Self-Assessment and Learning Progress Tracking
For students to engage meaningfully, they must understand what success looks like. Standards-based learning targets clearly define expected outcomes, while success criteria break those targets into measurable steps. This structure allows students to self-assess, remain focused, and reflect on their learning.
Example:
Learning Target: Analyze how an author develops ideas and connections within a text.
Success Criteria:
- I can identify the central idea
- I can explain how ideas are developed and connected
Students use these criteria to guide their work and evaluate progress, promoting deeper understanding and accountability.
Implement Systems to Monitor Daily Student Learning
Relying only on teacher observation can leave learning gaps unnoticed. Implementing structured systems such as checklists, rubrics, or digital platforms enables instructors to track whether students are achieving daily learning objectives and adjust instruction in real time. In fact, about 50% of higher education institutions now use AI-powered tools to monitor student performance, analyze engagement trends, and gain actionable insights to support learning outcomes.
Example:
Students can self-assess against defined success criteria during group activities, while instructors verify progress through observation and documentation. These results are recorded digitally, allowing educators to track growth over time and quickly identify areas where students need additional support.
Increase Academic Rigor Through Complexity and Autonomy
Engagement thrives when students are challenged with meaningful, rigorous tasks that require higher-order thinking and independent decision-making. Leaders can support teachers in designing tasks that balance cognitive complexity with student autonomy.
Key Elements of Rigor:
Complexity:
Tasks should align with or exceed the cognitive demand of learning standards, using frameworks like Marzano’s Taxonomy. Over-simplifying content reduces challenge and engagement.
Autonomy:
Students should have the freedom to explore, collaborate, and solve problems independently, with the teacher acting as a facilitator rather than the sole authority.
Example:
In a math lesson, student teams solve a complex problem and present different solutions. Instead of confirming the correct answer, the teacher encourages debate and reasoning. Students apply prior knowledge, defend their thinking, and collaboratively reach conclusions deepening both engagement and understanding.
Make Class Time Meaningful and Relevant
Students are more motivated when they can connect classroom learning to real-world applications. Relevance increases engagement by helping learners understand how concepts apply to careers, societal challenges, or personal experiences. Lessons that integrate authentic problems, case studies, or simulations foster critical thinking, problem-solving, and practical skill development.
Example:
In a business course, students collaboratively analyze real-world case studies, such as supply chain disruptions or marketing campaigns, and propose solutions. This not only teaches core concepts but also develops analytical, teamwork, and decision-making skills.
Invest in Faculty Development
Faculty effectiveness plays a crucial role in improving learning outcomes. Institutions that prioritize professional development equip instructors with the skills to implement innovative, interactive, and inclusive teaching strategies. Training in areas such as digital tools, gamification, active learning, and accessibility enables educators to meet diverse student needs while maintaining high-quality instruction. However, a recent survey found that about 68% of faculty feel their institutions have not adequately prepared them to use AI in teaching, mentoring, or research, highlighting the need for targeted faculty training.
Example:
Universities provide workshops on active learning techniques, virtual lab simulations, and LMS analytics, empowering instructors to design lessons that foster participation, collaboration, and meaningful student learning.
Collaborate with Students to Support Their Success
Engagement improves when students are active partners in their learning journey. By leveraging data from academic performance, attendance, and participation, advisors and instructors can provide personalized guidance. Collaborative planning helps students set realistic goals, track progress, and identify areas for improvement, fostering a sense of ownership over their education.
Example:
Advisors use student success platforms to create individualized learning plans, schedule milestone check-ins, and provide actionable feedback, ensuring that each student stays on track academically and professionally.
Provide Comprehensive Student Support Services
When institutions offer holistic support addressing academic, emotional, social, and financial needs, students can better manage external pressures and stay connected to the institution. Access to a wide range of resources helps them fully participate in learning experiences. AI-driven tools, such as virtual assistants, can handle routine inquiries efficiently, allowing staff to focus on higher-value support tasks while ensuring timely guidance.
Example:
Bakersfield College’s AI-powered virtual assistant has answered over 424,000 student questions, saving more than $2.2 million in staff time and significantly reducing inbound emails. Institutions offer tutoring centers, peer mentorship, counseling services, financial aid support, accessibility accommodations, student clubs, and cultural programs.
Leverage Technology to Enhance Learning and Enrollment Engagement
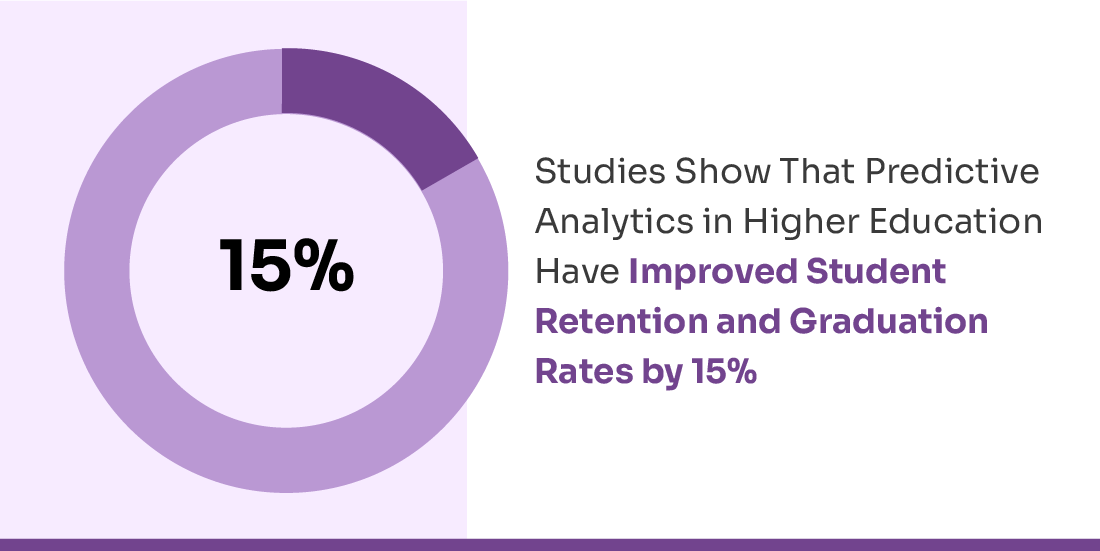
AI-powered educational technologies enhance accessibility, flexibility, and engagement starting from enrollment and continuing through the learning journey. Learning Management Systems (LMS), student portals, and intelligent digital tools centralize access to application updates, course content, assignments, discussions, and multimedia resources, ensuring students remain informed and connected at every stage. Advanced AI analytics monitor engagement patterns, identify students at risk early, and trigger personalized interventions, helping institutions support retention and academic success. Studies show that predictive analytics in higher education have improved student retention and graduation rates by up to 15%, demonstrating the effectiveness of data-driven engagement strategies.
Example:
From initial inquiry through enrollment, students access application updates, onboarding details, and academic resources through a single digital platform. EDMO’s Advisor Copilot enhances this journey by enabling admissions teams to deliver instant, 24/7 support across voice, SMS, and WhatsApp. By using engagement data to prioritize high-intent leads and personalize outreach, it keeps students informed and engaged while allowing staff to focus on meaningful interactions and faster enrollment decisions.
The Psychology Behind Student Engagement: Flow and Productive Struggle
Student engagement is about creating learning experiences that fully involve students and encourage active participation. Two key psychological concepts that explain high engagement are flow and productive struggle.
Flow: Total Involvement in Learning
Flow occurs when students are completely absorbed in an activity, feeling joy, creativity, and total focus. This state happens when tasks are challenging enough to stretch students’ abilities but still achievable with effort. When students experience flow, they are motivated to focus deeply, enjoy learning, and persist through challenges.
Productive Struggle: Learning Through Challenge
Productive struggle happens when students face problems or questions that are slightly beyond their current abilities. Instead of being given answers, students work actively to explore different approaches, test ideas, and find solutions on their own. This encourages critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and persistence.
How Flow and Productive Struggle Work Together
Both concepts emphasize a balance of challenge and skill:
- Challenge: Academic tasks that push students beyond their comfort zone
- Skill: Abilities developed through active learning and autonomy
When this balance is achieved, students stay engaged, motivated, and focused on meaningful learning.
Flow and productive struggle show why engagement is essential in learning. When students are given appropriately challenging tasks and the autonomy to solve problems themselves, they develop skills, confidence, and a love of learning.
Conclusion
In higher education, institutions that provide clear communication, personalized support, and technology-enabled learning create more effective and lasting learning experiences. By supporting students from enrollment through course participation, encouraging collaboration, offering timely feedback, and using data to monitor progress, universities can not only enhance academic performance but also boost retention and graduation rates. These strategies help ensure that students stay engaged, supported, and successful throughout their academic journey.








No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
Leave a Comment