Table Of Contents
Introduction
High school grades play a crucial role in college admissions. According to the National Association for College Admission Counseling (NACAC), in the Fall 2023 admission cycle, 77% of four-year colleges considered grades in college-preparatory courses as highly important, while 74% considered total high school grades similarly.
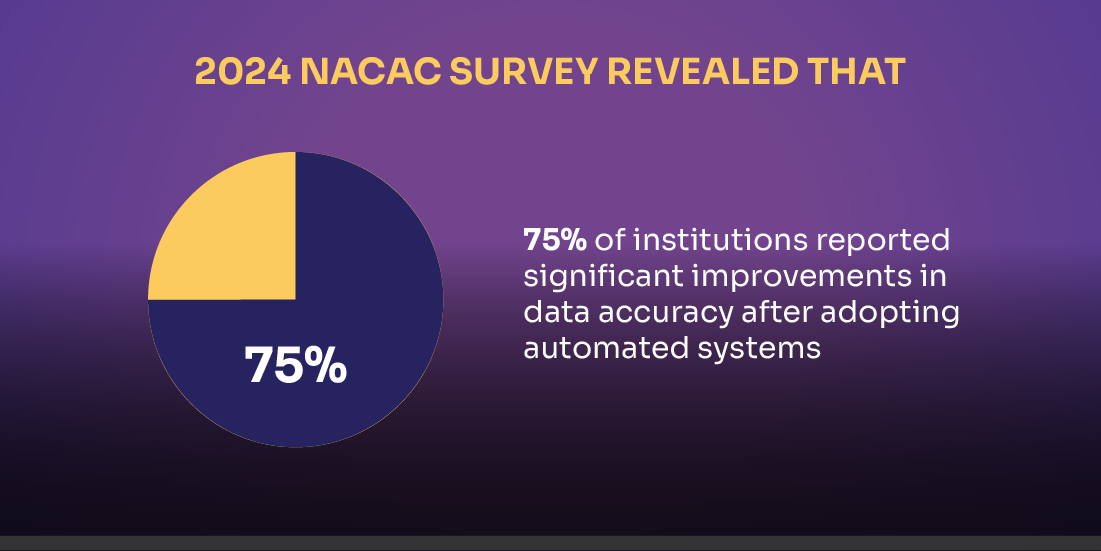
However, manually processing transcripts and calculating GPA in bulk is both time-consuming and error-prone. Recognizing this challenge, institutions are increasingly turning to automation. In fact, a 2024 NACAC survey revealed that 75% of institutions reported significant improvements in data accuracy after adopting automated systems. This highlights how AI-driven tools can not only streamline GPA calculations but also enhance reliability and fairness in the admissions process.
In this blog, we’ll explore how to calculate GPA in bulk quickly and accurately, saving time, reducing errors, and ensuring consistency across all applicants.
What is a GPA?
A Grade Point Average (GPA) is a standard way of measuring academic performance. It is calculated by adding together all the grades you earn across your courses and dividing that total by the number of credits attempted.
Most high schools and colleges use a 4.0 scale to report GPA:
- The highest grade, A, equals 4.0 points.
- Lower grades correspond to fewer points (for example, B = 3.0, C = 2.0, and so on).
Your GPA provides a single number that reflects your overall academic achievement and is often used by schools, universities, and scholarship committees to evaluate performance.
Why is GPA Important?
Your GPA (Grade Point Average) is more than just a number—it reflects your academic performance and can influence your future opportunities in many ways.
For High School Students
When applying to universities, your GPA is one of the first things admissions officers look at. Many universities have a minimum GPA requirement to ensure that applicants can handle the academic workload.
For University Students
GPA continues to play a significant role during your college years. It can affect:
- Scholarships and Financial Aid: Many scholarships require students to maintain a certain GPA. In the U.S., roughly 30% of all scholarships go to students with a GPA between 3.0 and 3.4, while only 4% go to those with a GPA of 3.5 or higher.
- Internships and Job Opportunities: Employers often use GPA as a measure of discipline and consistency, especially for competitive roles.
- Campus Involvement: Some clubs, honor societies, and leadership positions require a minimum GPA for membership.
- Postgraduate Applications: Whether applying for a master’s, MBA, or PhD program, admissions committees place strong emphasis on GPA alongside other achievements.
GPA Scale
Since GPA plays a major role in academics, here’s a simple chart to understand how letter grades convert to grade points on the 4.0 scale.
| Letter Grade | Grade Points | Numerical Grade Range |
| A+ | 4.0 | 97–100 |
| A | 4.0 | 94–96 |
| A- | 3.7 | 90–93 |
| B+ | 3.3 | 87–89 |
| B | 3.0 | 84–86 |
| B- | 2.7 | 80–83 |
| C+ | 2.3 | 77–79 |
| C | 2.0 | 74–76 |
| C- | 1.7 | 70–73 |
| D+ | 1.3 | 67–69 |
| D | 1.0 | 64–66 |
| D- | 0.7 | 60–63 |
| F | 0.0 | 0–59 |
How to Calculate GPA
Your GPA (Grade Point Average) is calculated by dividing the total number of quality points by the total number of quality hours.
GPA = Total Quality Points / Total credit Hours
Example:
If you earn 45 quality points over 15 quality hours, your GPA will be:
45÷15=3.000
Quality Points
Quality points are earned by multiplying the number of course credits by the numerical value of the grade received.
Example:
- A 3-credit course with a grade of B- (numerical value = 2.700)
- Calculation: 3×2.700=8.1 quality points
So, this course contributes 8.1 quality points.
Quality Hours
Quality hours represent the total credit hours attempted in courses that received a letter grade (A–F).
- Even if a student receives an F, those credits are counted as quality hours.
- However, courses with a grade of W (Withdrawal) do not count toward quality hours.
About EDMO GPA Calculator
Knowing how to calculate GPA accurately across different countries and grading systems can be challenging and time-consuming. EDMO’s AI-powered GPA Calculator simplifies this process, making it faster, more accurate, and fully standardized.
With seamless integration into CRMs like Slate and Salesforce, admins can manage everything from one dashboard. The tool displays total requests, student counts, batch uploads, and detailed reports. Users can begin instantly with manual entry, batch CSV uploads, or advanced OCR-based transcript scanning.
One of EDMO’s standout features is its rigor adjustment system, which accounts for institutional difficulty. For example, a 3.73 GPA from Oxford can be adjusted to 3.98, recognizing the academic rigor of the institution.
How GPA Is Calculated
Convert International Grades to U.S. Equivalents
Example: In China, a score of 90 = A, 85 = B, 80 = B.
Convert Grades to Points
Using the U.S. scale:
A = 4.0, B = 3.0, C = 2.0, D = 1.0, F = 0.0
(including plus/minus variations like A-, B+, C+, etc.).
Calculate Weighted GPA
Multiply the grade points by the number of course credits, add the results, and divide by the total credits
Example:
| Credits | U.S. Grade | Points |
| 3 | A | 4.0 |
| 3 | B | 3.0 |
| 2 | B | 3.0 |
- Total Points = (3 × 4.0) + (3 × 3.0) + (2 × 3.0) = 27.0
- Total Credits = 3 + 3 + 2 = 8
- GPA = 27.0 ÷ 8 = 3.38
With over 95% confidence in OCR accuracy, detailed filters, and audit-friendly reporting, EDMO’s GPA Calculator ensures precision and fairness whether you’re evaluating one student or thousands.
Cumulative GPA
Your cumulative GPA (also called overall GPA) is the most important GPA to know, as universities use it for applications, scholarships, funding, and even eligibility for certain clubs or organizations.
While you may have GPAs for individual semesters or classes, your cumulative GPA combines all of these to reflect your overall academic performance.
How to Calculate Cumulative GPA:
- Add up the GPA scores from all your classes or semesters.
- Divide the total by the number of classes or semesters.
- The result will give you an average GPA, usually between 0.0 and 4.0.
Weighted vs. Unweighted GPA
Whether your school uses a weighted or unweighted system changes how your cumulative GPA is calculated.
Unweighted GPA
- Each class is treated equally, no matter how difficult it is.
- The cumulative GPA is calculated by simply averaging all your grades.
- Maximum GPA is usually 4.0.
Weighted GPA
- Harder classes (like honors or advanced courses) carry more weight.
- This system rewards students for taking challenging subjects.
For example:
- A mid-level course might add +0.5 to the GPA score.
- An advanced course might add +1.0 to the GPA score.
- Weighted GPAs often use a 0.0–5.0 scale instead of the standard 4.0.
Read more: The Complete Guide to Education Technology Solutions
Conclusion
Understanding how to calculate GPA accurately is crucial for admissions teams, educators, and students alike. When dealing with large volumes of applications, manual calculations can be slow and error-prone. By using automated tools like EDMO’s GPA Calculator, institutions can calculate GPA in bulk quickly, maintain consistency, and ensure fairness across all applicants. In fact, a study from the National Association for College Admission Counseling (NACAC) revealed that 75% of institutions employing advanced technologies witnessed a marked decrease in administrative workload, further proving how automation enhances both efficiency and accuracy in the admissions process.











No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
Leave a Comment